A Complete Guide to Zero Trust Security

 By
Emily Miller
·
7 minute read
By
Emily Miller
·
7 minute read
Each year in the United States, entrepreneurs start over 600,000 new businesses. Unfortunately, not all of these companies reach the heights their founders intended.
Investing in effective business management tactics is an important component of running a successful business that all entrepreneurs should prioritize cybersecurity, but not everyone knows where to start. We've developed a quick tutorial that explains all of the essential things to consider.
Let's get started with what you need to know about zero trust security.
So, What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero trust security is a term for security models that don’t rely on predefined trust levels. Instead, they verify every user and device before granting access to data or systems. The goal here is to make it more difficult for cybercriminals to gain access to your network by eliminating the single point of failure that is inherent in traditional security models.
This applies to networks that are local, on the cloud, or a combination of the two. It also applies to workers across any possible location.
It's important to note that some businesses might have their own definitions of zero trust. However, the above information is considered standard across most industries.
How Does Zero Trust Security Work?
Zero trust security starts with the assumption that everyone and everything is untrusted.
This means that no one is automatically granted access to data or systems — not even employees or devices that are on the company network. Instead, each user and device must be verified before they’re given access to anything within the network.
As you might guess, this requires continuous monitoring. This is the only way to validate a specific user and their device. Zero trust architecture also requires a policy that establishes certain risks.
For instance, a user might be allowed to access certain data if their device is verified. However, they might not be able to access other data without this verification. In context, this means that all requests for access meet the standards of the zero trust architecture.
Common attributes for verification include geographic location, user identity, and type of device. Of course, these will depend on your business and its needs.
What Are the Benefits of Zero Trust Security?
There are many benefits that come with zero trust security that you shouldn't overlook. It’s much more difficult for cybercriminals to gain access to your network, as they would need to compromise every user and device on the network — not just one point of entry.
Additionally, zero trust can help you meet compliance regulations, such as those related to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Zero trust security can also save you time and money in the long run by preventing the compromise of sensitive data. To help put this into perspective, even a single data breach could cost a business hundreds of thousands of dollars. It could also erode the trust that customers and clients have in that company.
Finally, zero trust security can improve your company’s overall security posture. As more businesses adopt this type of security, the entire ecosystem becomes more secure.
Are There Any Risks Associated With the Zero Trust Security Model?
Of course, no security model is perfect.
Zero trust security is no exception. One of the biggest risks is that it can be difficult to implement. This is especially true for larger businesses with more complex networks.
Additionally, zero trust security can slow down processes as every user and device must be verified before access is granted. This can be frustrating for employees who are used to having immediate access to data and systems. As previously mentioned, zero trust security requires continuous monitoring.
This means that you’ll need to invest in the right tools and resources. Otherwise, you might not be able to properly verify users and devices. Finally, zero trust security is only as good as the people who are using it.
If employees aren’t following best practices, then the entire system can be compromised. For this reason, it's important that your employees receive proper training.
Interestingly, this is something that many firms neglect when implementing zero trust security.
How Do I Get Started?
The first step you need to take is to assess your current security architecture.
This will help you understand where your business currently stands and what needs to be improved. Once you have a good understanding of your current security posture, you can start to implement a zero trust model. This might involve making changes to your network infrastructure or investing in new security tools.
Of course, every business is different, so there’s no universal approach. You’ll need to tailor your zero trust security strategy to the specific needs of your business.
However, there are some general best practices that you can follow. For instance, you should start by identifying which assets are most critical to your business.
Then, you can focus on securing these assets. Additionally, you should create a comprehensive inventory of all the users and devices on your network. This will help you ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
Finally, you should continuously monitor your network for any suspicious activity. This way, you can quickly identify and respond to any potential threats.
What Are the Main Principles of Zero Trust Architecture?
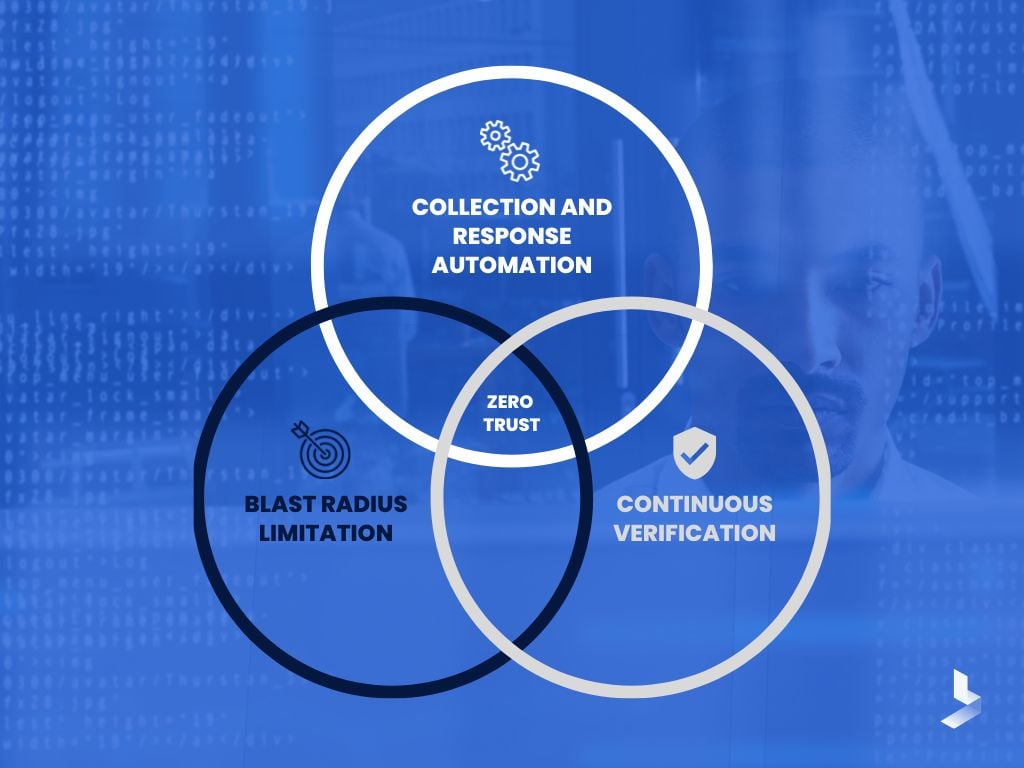
There are three main principles that all zero trust models should follow:
- Collection and response automation
- Continuous verification
- Blast radius limitation
Each of these plays a large role in determining how effective your IT security is. Let's take a closer look at each one below.
Collection and Response Automation
In order to save as much time as possible, it's important to automate the collection and response process.
This way, you can quickly identify and address any potential threats. Additionally, automation can help improve your overall security posture. By automating tasks like patch management, you can free up your staff to focus on more important tasks.
This will also make your security more efficient. For example, you will gain insight into security issues as soon as possible. From here, you can take the appropriate action without putting your data at risk.
The type of security data that you collected during this process includes user credentials, endpoints, workloads, and network information. This data also includes threat intelligence, which can help you prevent future attacks.
Continuous Verification
There are no trusted credentials or devices at any time. This means that just because someone has used a device in the past does not mean that it does not need to be verified again. This helps prevent attacks where someone compromises a device in order to gain access to sensitive data.
In order to continuously verify users and devices, you need to have a comprehensive inventory of all the users and devices on your network. This way, you can quickly identify any unauthorized individuals who might be trying to access your data.
You also need to have the right tools in place to properly verify each user and device. This might include two-factor authentication or biometric security measures.
These security measures must also be scalable. As you scale your business, so will your digital security needs. Without scalable verification, you will not be able to meet these rising standards.
Blast Radius Limitation
In the event of a breach, you need to limit the damage that can be done. This is known as blast radius limitation.
To do this, you need to segment your network into different zones. Each zone should contain data that is critical to your business. By doing this, you can contain the damage of a breach.
Additionally, you can quickly identify which zone was breached. This way, you can take the appropriate action to mitigate the damage. You also need to have the right tools in place to properly segment your network.
This might include a software-defined perimeter or a micro-segmentation solution.
How Can a Professional Help Me With a Zero Trust Model?
The primary way in which a professional can help you with a zero trust model is by conducting a comprehensive assessment of your IT infrastructure.
This assessment will help you identify any potential vulnerabilities in your system. Additionally, the assessment will help you determine which security measures are right for you. After the audit is complete, the firm you work with can help you implement the necessary changes to your IT infrastructure.
This might include installing the right software or making changes to your network configuration. The firm can also help you train your staff on how to use the new security measures. Lastly, they can provide ongoing support to ensure that your system remains secure.
How Do I Find a Cybersecurity Company That's Right For Me?
The first attribute you need to consider is their level of experience.
They should have significant experience conducting zero trust security audits at companies like yours. Additionally, they should be familiar with the different types of zero trust solutions. This way, they can help you choose the right one for your business.
Make sure that the cybersecurity company is reputable and has a good track record. You can check online reviews or ask for referrals from other businesses in your industry. Once you have narrowed down your choices, you should interview each firm.
This will help you get a better understanding of their services and how they would approach your specific situation.
When Should I Implement a Zero Trust Model?
There is no single answer to this question. The best time to implement a zero trust model is when you are ready to make a commitment to improving your security posture.
This might be in response to a security incident or as part of a larger digital transformation initiative. You should consider implementing a zero trust model if you are moving to the cloud or if you are working with sensitive data. You should also use a zero trust model if you are required to comply with certain regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
How Much Does It Cost to Implement a Zero Trust Security Model?
The cost of implementing a zero trust model will vary depending on the size and complexity of your IT infrastructure. Additionally, the cost will depend on the security measures you choose to implement.
Generally speaking, you can expect to spend between $5,000 and $100,000 on zero trust security solutions. The professional that you work with can help you get a better understanding of what you need to budget for.
Key Takeaways
A zero trust security model is a type of security that does not rely on pre-existing trust relationships. There are three key components to a zero trust security model: identity verification, blast radius limitation, and least privilege.
A professional can help you assess your IT infrastructure and determine which security measures are right for you.
When choosing a professional, make sure that they have significant experience with zero trust security models and are familiar with the different types of solutions. Be sure that you keep this information in mind when you make your decision
How Can BitLyft Help?
We aim to monitor and detect threats 24/7. This allows us to protect businesses from issues they may have suffered from otherwise, such as data breaches. We also gather threat intelligence to improve our security strategies and make them more effective as time goes on.
Our solution is also highly scalable and offers continued support to meet your needs.

Zero Trust Security Doesn't Have to Be Complicated
Incorporating zero trust security might seem complex, but it's easier than you might expect it to be. Keep the above guidelines in mind so you can avoid problems you may have otherwise dealt with.
Want even more information to learn about cybersecurity systems? Sign up for our email newsletter.
