AWS SIEM Use Cases: A Look at Security Monitoring and Analytics

 By
Emily Miller
·
10 minute read
By
Emily Miller
·
10 minute read
We've been experiencing an explosion of cybersecurity-related issues these last few years. 2021 set a new record for the amount of data breaches in a single year, with over 18.5 million records exposed. Cybersecurity is clearly of the utmost importance.
Yet so many don't know how to set up and configure their cybersecurity correctly. A staggering 81% of companies report the costs of staying ahead of cybercriminals is unsustainable. AWS SIEM use cases help prevent this by showing you exactly how to set your SIEM solution inside AWS.

What Is AWS SIEM?
Let's start by defining our terminology. AWS SIEM stands for Security Information and Event Management. It's Amazon Web Services' built-in solution for security monitoring and raising security alerts when there's an issue.
AWS SIEM creates detailed logs of any incidents your AWS security management system detects. This is essential to ensure your cybersecurity solutions are as robust and as comprehensive as possible.
AWS SIEM is like traditional cybersecurity but then catapulted into warp speed. It takes traditional cybersecurity solutions, like malware detection, and then pairs it with the latest, most cutting-edge innovations like machine learning and artificial intelligence.
This allows SIEM to catch potential cybersecurity incidents that other more rudimentary security tools might miss. Modern technology lets SIEM make use of the latest in pattern recognition and advanced user profiles to create detailed models that catch virtually everything out of the ordinary that's happening on your network.
AWS SIEM requires a bit of a paradigm shift, as it's such a departure from traditional location-based cybersecurity. Cloud-based services such as AWS are not affixed to one geographic area, for example. This brings its own logistics in terms of data compliance and governance.
It also means that users might be signing in from all over the world as well. This makes traditional cybersecurity techniques like geolocation restriction troublesome to implement. Which is where AWS SIEM comes into play.
Advantages of AWS SIEM
Before we delve into some real-world examples of AWS SIEM, let's pause for just a moment and consider a few more reasons you should consider SIEM for AWS over other cybersecurity tools.
Faster Than Other Tools
When there's a cybersecurity incident, it's imperative that you respond as quickly as possible. When there's been a data breach or your network is at risk of being infected by malware or ransomware, every second counts.
AWS SIEM empowers your IT team to respond to cybersecurity threats in a number of different ways. First of all, SIEM for AWS can alert you and your security team as soon as there's an incident.
SIEM is also constantly updating itself, so it stays up to date with the latest security tech and trends. You won't have to worry about installing patches or running manual updates. AWS SIEM does all of that for you.
Improved Reporting
Old-fashioned cybersecurity risks like trojan horses, malware, or external attacks aren't nearly as common as some of the more modern security threats. Your network is far more at risk of being effected by a phishing email, judging from stats reported by the healthcare industry.
These shifts in the cybersecurity sector means far more robust and detailed reporting is needed to truly see what's happening during a cybersecurity threat. Charting a cybersecurity risk is the only way to truly prevent these threats from happening in the future.
Rather than simply relying on an external firewall that surrounds your entire system, AWS SIEM lets you put firewalls in place throughout your network. You might put one around your system files, for example, so you can keep a log of anyone who attempts to access or modify those files.
These data logs are rich in both data and context. The data returned from this security management system can reveal where a particular user-agent goes after breaching the security perimeter following a DDoS attack, for example.
In some circumstances, this reporting can even offer hints about where the security vulnerability was coming from in the first place.
More Accurate Data
If you have any hope of preventing cybersecurity incidents, it requires good data. Insufficient security solutions often fail to recognize threats when they happen. This means these threats never get logged at all.
Just as importantly, SIEM normalizes all of your security data into one standardized format. This makes it exponentially faster to analyze and assess security logs no matter where they're coming from. This is true for computers and IT professionals alike.
Better Network Visibility
Modern networks are complex. It's far too common to have some corner of your network you simply forget exists. Unfortunately, these shadow regions of your system are perfect for exploitation from cybercriminals.
SIEM normalizes data across your entire organization and network. This standardized format makes it far less likely to overlook sections of your network.
This standardized format extends to all of your databases, servers, devices, and third-party applications.
Enhanced Data Compliance
The prevalence of data breaches in recent years has greatly increased the demand for improved data compliance and governance. SIEM solutions illustrate your data and network in a standardized format so you can prove your compliance to the governing bodies.
AWS SIEM Use Cases
Now that you've got an idea of how AWS SIEM functions, in general, let's take a closer look to get a better idea of how SIEM for AWS functions in real life. One of the problems facing a lot of people running and maintaining today's networks and systems is how complex and abstract they can be.
As a brief example, consider microservice-based containers implemented on the cloud. Even for network administrators more used to physical systems can sometimes have a hard time conceptualizing these new technologies.
Instead, imagine having a cloud-based security system based out of Europe. European countries have their own rules and laws around data compliance like GDPR or HIPAA.
Then maybe you might have a similar container-based system running in Asia. Asian countries will each have their own laws around data compliance, as well. In those scenarios, each geolocation might have its own configuration based on the region's laws.
This is just one example of how high tech terminology becomes much more concrete and practical once you see it in action.
Before we get into some specific cases, let's take a moment to consider how AWS SIEM is set up, in general. These understanding will be important to help you conceptualize how to best implement SIEM for AWS.
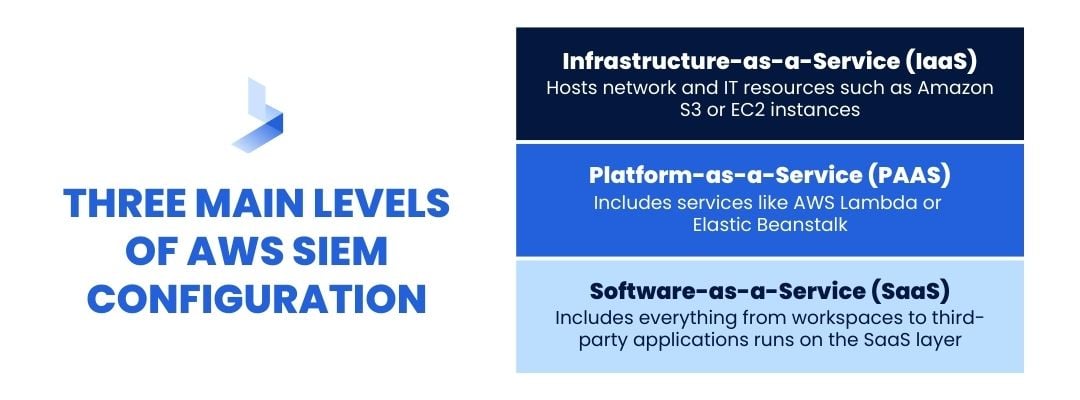
How AWS SIEM Is Configured
AWS SIEM is organized around three main levels. First, you have Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS). The IaaS layer often hosts network and IT resources such as Amazon S3 or EC2 instances.
Next up is the Platform-as-a-Service (PAAS). Infrastructure management systems tend to run on the PaaS layer. This includes services like AWS Lambda or Elastic Beanstalk.
Finally, there's a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) layer. The SaaS layer is the level most commonly accessed by end users. Everything from workspaces to third-party applications runs on the SaaS layer.
AWS SIEM Monitoring
To understand AWS SIEM in action, it's useful to have an understanding of how AWS SIEM monitoring is set up as well. AWS SIEM monitoring is the nervous system that ensures your network is safe and secure.
First you have the Control Panel Logs. These are the logs for anything that's used to control your network. This could be anything from AWS EKS to AWS CloudTrail.
Then there's the Network Communication Logs. This keeps a record of any communications that occur across your network. This could be from anywhere from VPC Flow Logs to AWS ELB.
Next, there's the OS and Application Logs. These are records from operating systems and applications like Cloudwatch.
Finally, there's the Alerts. Alerts are any signals from any security solutions you're running in your AWS environment.
Where To Get AWS Data
AWS SIEM is only as good as the data that drives it. It's important to know where to get data from your AWS system to ensure your SIEM is set up correctly.
AWS Cloudtrail collates data from all over your AWS system. This could be anywhere from your AWS Management Console to any SDKs you're running on your network.
AWS Cloudtrail can even compile data from your command line applications.
Data from your monitoring solutions can be integrated into your SIEM solution, also. Data from Amazon CloudWatch is an invaluable source for your SIEM logs.
Finally, cloud storage and log aggregators like Amazon S3 can also be integrated into your SIEM strategy.
Now let's take a deeper look at some AWS SIEM use cases. These SIEM use cases will give you a better idea of what you need to be monitoring. They'll also give you some ideas about useful data sources to feed your security logs.
AWS SIEM Use Cases #1: Apps
Let's start off by visualizing some apps you're running on your AWS environment.
First, imagine you're running a series of SaaS tools for your team and a small handful of users. For the sake of argument, imagine it's a Windows-based server.
This one app generates numerous levels of data logs. This one application could feature a systems log, security log, application log, and IIS log.
On the same network, you might be running a VPC. This generates a VPC flow log. Applications like AWS Lambda might be generating data on this network, as well.
Finally, you could have an application like Amazon EK5. Amazon EK5 might generate everything from Kube-apiserver logs to audit logs to authenticator logs and scheduler logs.
Now you start to see AWS SIEM in action.
All of these disparate data sources are then filtered through Amazon CloudWatch via CloudWatch Agent. Once all of these log sources are collated into one central location, Amazon CloudWatch can then analyze them all, at once, using CloudWatch Connector.
Each of these data streams is known as a Log Stream. Log Streams can be grouped together, as well, into Log Groups.
There are numerous protocols in place to ensure that AWS SIEM is secure, as well. Users are often required to have numerous levels of access, from an access key ID to the name of the specific log streams and log groups they're attempting to access.
AWS SIEM Use Cases #2: CloudTrail
Almost every AWS service communicate using API calls. All of these API calls can be logged, monitored, and tracked using AWS CloudTrail.
Imagine you're running an Amazon RDI, an Amazon VPC, and a security application.
Each of these services communicates via an API. These API calls are then routed through AWS CloudTrail. Once they're in CloudTrail, these API calls can be integrated into SIEM using an S3 SQ5 connector.
AWS SIEM features numerous ways to keep this log data secure. Users need to have an access key ID as well as a secure access key in order to access this data.
AWS SIEM Use Cases #3: AWS S3
AWS S3 is able to integrate data from all manner of different applications. You might have security data from a web application, for instance. You might also have a data stream from something like CloudFront.
All of these different applications can be connected to AWS S3 via a series of connectors. This is incredibly convenient, as some applications like CloudFront stores its data in proprietary formats, such as compressed data. All of the connectors need to take that data from all those different sources and consolidate it into a consistent format.
Once it's been collated in AWS S3 it's ready for your SIEM. AWS S3 can be connected to your SIEM using the S3 SQ5 Connector.
Once the data's inside your SIEM, it's secure unless you have the access key ID, secret access key, and specific SQ5 Queue URL.
AWS SIEM Use Cases #4: Compromised User Credentials
There are numerous ways a user's credentials could be compromised. These range from Brute Force tactics to Pass the Hash or Golden Ticket. Tracking compromised user data is tricky, as it often comes from valid users. These users' accounts are just being used in unauthorized ways.
This is one of the main reasons why you need SIEM, though. SIEM can pick up on suspicious user behavior in ways that standalone security applications simply can't.
The first step in these SIEM use cases for AWS starts with recognizing a suspicious user. Once that user's been marked as suspicious, though, it's vital to see what that user's done to help gauge the extent of the damage they may have wrought on your system.'
An example of a compromised user credential SIEM flow might look like:
[label=User label=Login label=Successful logon_type=9 package=Negotiate logon_process=seclogo] as s1 followed by [norm_id=WindowsSysmon label="Process" label=Access image="*lsass.exe" access="0x1010"] as s2 within 5 second on s1.host=s2.host | rename s1.host as host, s1.user as user, s1.targetoutboundusername as target_user, s2.process as "process" | chart count() by user, target_user
AWS SIEM Use Cases #5: Charting System Changes
System changes can also be notoriously challenging to guard against. Once someone has access to your system and network, they can move a lot of files. They can change a lot of file permissions.
Even worse, these changes can have some of the most devastating effects of anything that can happen to your network. Safeguarding against situations like this requires a sophisticated, nuanced AWS SIEM system.
Even more, it's imperative that these unauthorized system changes are detected and stopped as quickly as possible. Otherwise, the unauthorized user can alter the log files and you'll never be able to tell that an unauthorized change has taken place.
In fact, modifications to an audit log is one of the alerts you can set in your SIEM workflow. Anytime someone attempts to alter an audit log should be worthy of notice, at the very least.
An example of charting unauthorized system changes might look like:
label=Log label=Clear | chart count() by log_ts, host, user, target_channel
AWS SIEM Use Cases #6: Detecting Unusual Behavior
The ability to detect anomalous behavior from a user with elevated access privilege is one of the most important reasons to have AWS SIEM, as you can see from this AWS security management system use case. Detecting such behaviors requires having an advanced mathematical model of a user's behavior in place on top of having detailed records of a user's history.
There are various ways AWS security management might pick up on this unusual behavior. The system might detect that the user has logged in from an unusual IP address, for example. Even an unexpected user-agent string could be a sign that something's wrong.
An example of a script for detecting unusual behavior from a privileged account is:
[norm_id=WinServer label=User label=Login label=Remote host IN WINDOWS_DC user IN ADMINS] as s1 followed by [norm_id=WinServer label=User label=Login label=Remote -host IN WINDOWS_DC] as s2 within 10 minute on s1.user=s2.user | rename s1.host as domain_controller, s2.host as host, s1.user as user, s1.domain as domain | chart count() by domain_controller, host, user, domain
AWS SIEM Use Cases #7: PCI Compliance
Earlier, we talked how important data compliance has become in the wake of a global outbreak of data breaches. Different industries have different requires for data compliance, however.
The Payment Card Industry (PCI) created the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) in order to help prevent data fraud and unauthorized usage. The PCI DSS dictates 12 different areas where service providers can help ensure that a user's data is as secure as possible.
These standards apply to everyone from merchants to credit card processors to third-party service providers.
AWS SIEM can be used to enhance PCI DSS compliance in numerous ways. The first is by using perimeters around your entire network in order to detect unauthorized access attempts.
Monitoring user identities can also help to prove compliance. This method can be used to illustrate suspicious or unauthorized behavior even from authorized users.
AWS SIEM can be used for real time threat detection, as well, which is one of the most common applications for the cybersecurity solution. AWS SIEM can monitor antivirus logs as well as vulnerable ports in search of threats to your network.
It can monitor for unauthorized usage of data or production systems by looking for generic credentials or unauthorized reproductions of production systems.
AWS SIEM Use Cases: Final Thoughts
The world is never going back to an analog state. Things are only going to become more and more data-driven and automated as the years progress.
This means cybercriminals are going to adopt the latest cutting-edge technology to gain access to all of that valuable data. Cyberattacks like ransomware are only going to become increasingly prevalent, as well, if the last few years are any indication.
Fortunately, these same technological tools can be used to safeguard our companies and data. AWS SIEM is able to use sophisticated machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms to know your users even better than they know themselves.
Unfortunately, however, this same sophistication can sometimes make it seem like you're reading computer science journals or whitepapers instead of simply looking for a rugged, robust cybersecurity solution. Hopefully, seeing these AWS use cases can help make these concepts a bit more concrete and a bit less abstract.
Once you get used to AWS SIEM, it becomes second nature, especially when you've got a full team of cybersecurity experts on your side!
Are You Looking For NextGen Cybersecurity?
Threats to your cybersecurity are constantly evolving. Your cybersecurity needs to evolve even faster if you want to ensure your network and data remain safe and secure.
At BitLyft, it's our passion to ensure our clients have the latest, most cutting-edge cybersecurity tools and features. Knowing that your network is safe and secure gives you the peace of mind you need to focus on building your business and delivering world-class customer service.
Now that you've read some AWS SIEM use cases for yourself, you're ready to find out how state-of-the-art cybersecurity can empower your business and make it nearly impervious to nearly anything. Get started today, and put all of your worries about data breaches and ransomware to rest!
