The State of Healthcare Cybersecurity: Top Insights and Trends

 By
Emily Miller
·
7 minute read
By
Emily Miller
·
7 minute read
Cybersecurity is a critical concern for businesses across all industries. Yet, the healthcare sector is in a class of its own when it comes to the dangers and vulnerabilities associated with cyberattacks. Healthcare facilities are attractive targets for attackers because they house a massive inventory of sensitive data and downtime is particularly dangerous. While digital transformation is a vital step in providing patients with improved healthcare services, these changes present additional vulnerabilities ripe for exploitation by hackers.
Healthcare institutions are tasked with maintaining the safety of patient data and keeping operations running smoothly to protect patient health. Cyberattacks in healthcare lead to the theft of sensitive patient information and are a threat to patient safety. Unfortunately, attacks in the sector continue to increase exponentially. While global cyberattacks increased by 38% in 2022, attacks in healthcare increased by a whopping 86%. For healthcare facilities to protect against the growing number of attacks, increased education and a layered approach to cybersecurity are crucial.
This blog explores key trends driving attacks and emerging cybersecurity practices assisting healthcare facilities in the protection against attacks. We'll discuss vulnerabilities propelling increased attacks and outline best practices for strengthening healthcare cybersecurity.
The Growing Threat Landscape in Healthcare
Limited budgets for cybersecurity, immense pressures related to pandemic challenges, and a wealth of high-value data make healthcare facilities prime targets for cybercriminals. Data breaches in the healthcare sector have climbed for the past five years, rising a massive 42% in 2020 when the pandemic hit. Even as the effects of COVID-19 wane, attacks haven't slowed. Healthcare data breaches affected over 22.6 million total patients in 2021, with the largest breach affecting over 3 million individuals and several other attacks affecting over a million patients. Unfortunately, these numbers fail to account for hundreds of smaller incidents and those that go unreported. Attacks continued to rise in 2022, with an average of 1,410 weekly attacks per organization, and 25% of all ransomware attacks targeted at healthcare. The most prolific cyberattacks on healthcare facilities include phishing, ransomware attacks, data breaches, and DDoS attacks.
 Cyberattacks in recent years have exploited supply chains, targeted vulnerable IoT devices, and compromised the sensitive data of millions of patients. Some of the most notable attacks include:
Cyberattacks in recent years have exploited supply chains, targeted vulnerable IoT devices, and compromised the sensitive data of millions of patients. Some of the most notable attacks include:
- Accellion FTA hack: Launched by the Clop ransomware group in 2021, the data breach impacted over 100 companies and over 3.51 million individuals. Attackers exploited longstanding, zero-day vulnerabilities in legacy systems and unpatched software to launch the attack and steal sensitive information used to extort victims.
- CommonSprit Health Attack: The 2022 attack compromised the personal data of over 600,000 patients, including electronic medical records. As a result, a 3-year-old patient was mistakenly given five times the amount of medication he was prescribed. While the patient made a full recovery, the incident highlights the potential for fatal results caused by attacks on healthcare facilities.
- Advocate Aurora Health Attack: The improper use of a common website tracking device led to the exposure of the data of 3 million patients in July of 2022.
- University of Vermont Medical Center Attack: In October 2020, a phishing email led to a ransomware attack that forced officials to shut down all internet connections. The attack encrypted 1,300 servers and deposited malware on 5,000 devices. While no patient data was compromised, it took 28 days to rebuild the infrastructure and several more months to restore the entire system.
Cyberattacks on the healthcare industry yield higher profits for criminals, as health information can fetch about $1,000 per record on the dark web (compared to about $5 per credit card number and $1 per social security number). Attacks can also lead to extreme consequences for healthcare institutions and the patients who depend on them. Cyber incidents can obstruct operations and patient care, resulting in delayed surgeries and diverted ambulances.
A study conducted by the Ponemon Institute revealed that the most common cyberattacks on facilities resulted in increased mortality rates for 23% of organizations. Furthermore, poor patient outcomes were reported by 57% of surveyed organizations and nearly half reported increased complications from medical procedures. On top of these dangers, healthcare facilities lose millions due to system damages, ransomware payments, and lost productivity. Cybercriminals are aware of the urgent nature of these consequences and depend on the grave nature of such consequences to yield a rapid and lucrative response.
Key Trends and Insights in Healthcare Cybersecurity
To effectively protect healthcare institutions, it's essential to investigate the reasons behind attacks and potential solutions to thwart attackers. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve in the digital transformation and the cybersecurity landscape increases to exploit new vulnerabilities, specific trends emerge. By tracking these trends, organizations can improve their cybersecurity posture to better protect against all types of cyberattacks.
These are some of the trends driving increased attacks and changes in cybersecurity methods in the healthcare sector.
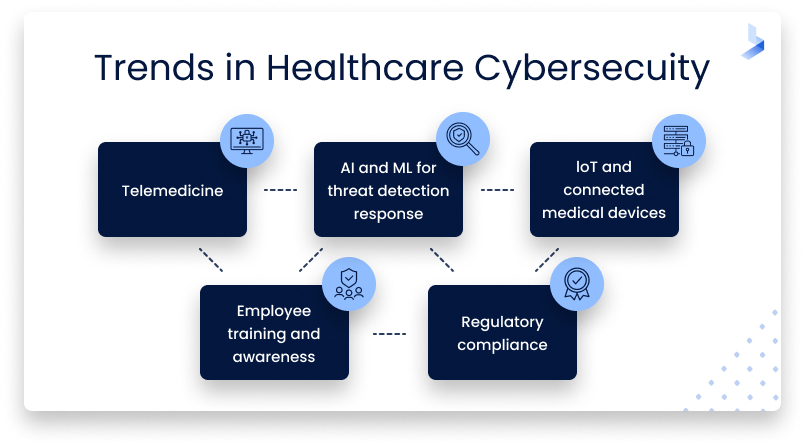
The Rise of Telemedicine
Telehealth use has grown exponentially in response to COVID-19. The convenience and reduced cost of these services make the continued use of virtual health services inevitable. Telemedicine includes virtual appointments, monitoring with the use of medical devices, and data sharing over cloud connections. Virtual healthcare allows short-staffed medical teams to treat more patients and helps patients spend less time in healthcare facilities and hospitals. However, cloud-based communications and data transfer alongside the vulnerabilities presented by remote devices used in telehealth services represent increased cybersecurity risks. Protection against threats to secure telemedicine platforms is complex and requires a layered security approach and buy-in from stakeholders.
The Growing Adoption of IoT and Connected Medical Devices
Hospitals and healthcare facilities use dozens if not hundreds of IoT devices including wearable medical devices, guided imagery, monitoring sensors, implants, etc. These devices allow healthcare professionals to assist and monitor patients remotely for convenient and cost-effective services. The success of such devices and accelerated use due to pandemic restrictions has resulted in the exponential growth of IoT devices in healthcare, with values expected to surpass $467.25 by 2027.
To store and share information, IoT devices are connected to a cloud-based network that can be vulnerable to attacks. Medical practices with more than 70% of their devices connected are 24% more likely to experience cyberattacks than practices with 50% or fewer connected devices. Connected devices expand the attack surface of an organization because IoT devices often go unmonitored for vulnerabilities. Furthermore, necessary precautions are often ignored. For example, 57% of healthcare organizations don't always change default usernames and passwords for medical devices, and 82% run connected devices on legacy systems.
AI and ML for Threat Detection and Response
As healthcare continues to experience rapid digital evolution, attackers will continue to target new systems. Cybercriminals use a variety of covert methods and highly technical tools to launch successful attacks on the healthcare industry. To build an effective defense, healthcare institutions must invest in powerful tools to detect and respond to such attacks.
Tools that utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being recognized for their abilities to detect and quickly mitigate cyberattacks. The 2022 Cost of a Data Breach Report revealed that organizations using AI and automation had a 74-day shorter breach lifecycle and saved an average of $3 million more than those without. AI-based cybersecurity tools like security information and event management (SIEM) and security orchestration automation and response (SOAR) enable healthcare facilities to reduce vulnerabilities, maintain compliance, rapidly detect suspicious behavior and immediately respond to attacks. As a result, successful attacks can be reduced.
The Importance of Employee Training and Awareness
Risk management strategies are an essential part of preventing attacks in healthcare facilities. As digital environments evolve in healthcare institutions, it's essential to take steps to reduce the vulnerabilities introduced to organizational networks. Healthcare professionals carry the burden of learning to use new tools and devices in a rapidly changing environment dependent on the flawless execution of services. Such a heavy load of responsibilities can make security an afterthought.
Employee awareness and training introduces employees to the potential security risks posed by new tools, devices, and applications used in an institution. It also provides essential information about how to recognize common attacks like phishing. Attacks demand fast responses which can be even more urgent in the healthcare industry. Institutions that arm employees with information about vulnerabilities and attack methods, enable them to avoid falling victim to common attacks.
The Role of Regulatory Compliance
The HIPAA Privacy Rule creates national standards to protect individuals' medical records and other personal health information. Alongside giving patients more control over their health information, it establishes appropriate safeguards that healthcare providers must achieve to protect the privacy of health information. When healthcare facilities don't take adequate measures to protect the private personal information (PPI) of patients, they fail to comply with HIPAA regulations. A successful data breach could signal non-compliance.
HIPAA requires healthcare professionals to reasonably protect patient privacy by setting up safeguards on all equipment, data storage devices, administrative software and computer systems, as well as proper cybersecurity protection. To achieve this, HIPAA requires organizations to take the following security measures.
- Risk Analysis and Management:
- Administrative Safeguards
- Physical Safeguards
- Technical Safeguards
- Organizational Requirements
- Policies and Procedures
In short, the HIPAA Privacy rule outlines how healthcare facilities must protect patient information. The actions described in the rule can act as a roadmap to help institutions achieve improved cybersecurity amidst digital adoption.
Best Practices for Strengthening Healthcare Cybersecurity
A wealth of valuable sensitive data, vulnerable systems, limited cybersecurity budgets, and a low tolerance for downtime make healthcare facilities an attractive target for cybercrime. To mitigate the expense and dangerous effects of cyberattacks in the healthcare sector, it's essential for organizations to take steps to improve cybersecurity.
Invest in a Comprehensive Security Solution
In today's modern threat landscape, it's essential to invest in a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity that includes highly capable technical tools combined with the expertise of cybersecurity professionals. Managed Detection and Response (MDR) is a complete cybersecurity solution that provides businesses and organizations with customized services designed to rapidly detect threats, analyze danger, investigate damage, and automatically contain and mitigate threats.
MDR provides healthcare institutions with better visibility into extensive digital networks and automated tools to detect and respond to attacks. It helps organizations identify assets and keep them secure. The services can even be customized to improve compliance with HIPAA and other industry regulations. Most importantly, MDR empowers an organization to act quickly in the face of an attack with the help of a remote team of cybersecurity professionals.
Adopt Best Practices for Cyberattack Prevention
Phishing accounts for over half of all cyberattacks in the healthcare industry. Unpatched vulnerabilities and risky practices account for 82% of successful cyberattacks across all sectors. User error is a critical danger in cybersecurity that can't be mitigated by software or tools. Lax security practices and errors invite attackers past security perimeters to access the network. The importance of cybersecurity best practices can't be overstated in the fight against modern cybersecurity attacks.
These strategies can help you improve your cybersecurity posture and protect against attacks.
- Conduct routine scans to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Always apply software patches and updates immediately.
- Train employees regarding phishing and other common attacks.
- Maintain offline, encrypted backups of data and regularly test backups.
- Improve third-party security by checking security ratings and conducting risk assessments.
- Implement multi-factor identification to require network users to use multiple forms of ID to access devices and information.
Improve Collaboration Across the Entire Sector
Effective cybersecurity in healthcare is a critical need that affects everyone. Successful attacks limit the abilities of healthcare facilities to provide life-saving care to patients. In the recently released National Cybersecurity Strategy, the Biden Administration put out a call to defend critical infrastructure. Beyond adopting minimum cybersecurity standards, the policy calls for collaboration between organizations, cybersecurity vendors, and government agencies.
In the healthcare industry, it's essential for institutions to invest in third-party services to better protect against attacks. Collaboration for cybersecurity in healthcare includes sharing critical information, adopting the required security standards, and working across organizations to build a more resilient defense for the industry as a whole.
Cybersecurity Prioritization is Crucial to Avoiding Dangerous Attacks in Healthcare
The evolution from pen and paper to a digital environment in the healthcare industry has dramatically improved opportunities for high-quality safe and effective healthcare. These advances also present vulnerabilities hackers can exploit to launch dangerous and expensive cyberattacks. To protect patients and the critical infrastructure provided by the healthcare sector, it's essential to make cybersecurity a priority in healthcare.
Healthcare institutions can't afford to wait and see what damaging impacts the next cyberattack might bring. When downtime and lost patient data can lead to catastrophic results, healthcare institutions are bound by responsibility to prevent cyberattacks to the best of their capability.
Want to secure your clinic with the best protection? Download our free MDR Buyer's Guide now and learn how Managed Detection and Response security can safeguard your healthcare facility from cyber threats.
