The True Cost of a Security Breach

 By
Emily Miller
·
11 minute read
By
Emily Miller
·
11 minute read
The effects of a security breach last far beyond the time it takes to contain and remediate the attack. According to the 2021 Cost of a Data Breach report, the cost of a data breach in 2021 was 4.24 million, a 10% increase from 2020. This figure is derived from a global average of reported attacks. Yet, data breaches in the US are vastly more expensive than in other countries with the average cost totaling around $9.05 million (more than double that of the global average). The report takes into account many different cost factors including legal, regulatory, technical activities, customer turnover, etc. While this is a good indication of the severity of data breaches, it is still difficult for many organizations to recognize the true impact and related cost of a security breach.
When a data breach occurs, an organization will face certain upfront costs like ransom demands, investigation into the attack, and remediation to repair and secure the network. After all of this is taken care of the attack is over. Yet, the aftermath of the breach is just beginning. The effects and related costs of a data breach can affect an organization for several years after the incident is contained. Often, the ongoing costs are far more than a ransom or the upfront costs of responding to an attack. As a result, it's practically impossible to accurately define the true cost of a data breach for an individual organization.
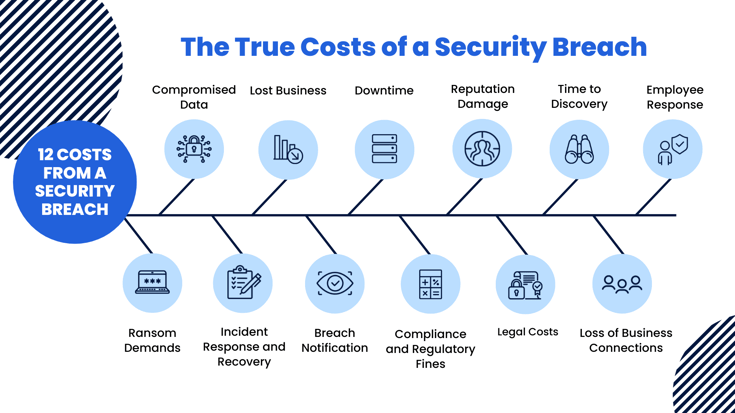
In a broad sense, the costs of a data breach can be broken up into expected and hidden costs. However, each can be difficult to quantify, and some costs are completely overlooked. The true costs of a data breach can last well into the future and should be recognized by every business. If your organization has never experienced a data breach, consider how these costs will affect your business.
- Ransom Demands
- Compromised Data
- Incident Response and Recovery
- Lost Business
- Breach Notification
- Downtime
- Compliance and Regulatory Fines
- Reputation Damage
- Legal Costs
- Time to Discovery
- Loss of Business Connections
- Employee Response
Ransom Demands
This is the most obvious cost and is often the cost described in news stories and reports. Ransom payment demands are always rising, with the average ransom demand totaling $220,298. The requests for outlandishly high payments more than doubled from 2020 to 2021, as the number of companies that paid a ransom of $1 million or more rose from 4% to 11%. Equally as concerning, the percentage of organizations paying less than $10,000 dropped to 21% from 34%.
Although authorities recommend that victims never pay the ransom, many pay up to decrease downtime. The reality is, paying the ransom doesn't ensure that your data will be immediately restored. Even worse, data could be permanently corrupted even after it is restored. Paying a ransom sends the message that ransomware works, fueling the increasing attacks that occur each year. Most often, payment doesn't yield faster decryption results. It could even lead to a second attack, as 80% of organizations that paid were hit by ransomware a second time, with 68% saying the second attack came less than a month later and threat actors demanded a higher ransom amount. When a data breach includes a ransom request to stop hackers from leaking/selling sensitive customer data, there is no guarantee the information won't be leaked upon payment.
Often, ransomware demands vary by the industry of the organization and financial records. In other words, cybercriminals do their homework and request a ransom that the company is more likely to pay. The typical ransom demand is between 0.7% and 5% of the victim's annual revenue. Many hackers offer discounts for ransoms paid within a few days.
Compromised Data
All information has value. The types of information most commonly targeted during a data breach are intellectual property (IP) and personally identifiable information (PII). The information is valuable for different reasons.
An organization's IP holds the secret to its current or future success. Intellectual property includes works and inventions that are a result of innovative thinking. In other words, the IP of a successful company cannot be reproduced. Losing IP can devastate a company's growth and cause the value of the company to decline. Stolen trademarks, patents, copyrights, and trade secrets can derail a company's future. For that reason, it makes the perfect target for a high ransom demand.
As a business, you have certain responsibilities to protect the personally identifiable information customers share with you. Unfortunately, Customer PII is the most expensive and frequently compromised data in a breach. PII is valuable because it can include the victim's name, driver's license information, social security number, financial records, and medical records. When stolen, the information can be used to apply for loans, credit cards, or even passports in the victim's name. Savvy attackers could reach out to the victims to extort money or gain access to their online accounts. In the event of a successful breach, hackers often steal this data and sell it for an admirable lump sum on the dark web. For the victim, stolen customer records can drastically increase the cost of a data breach. Successful companies can store the PII of hundreds, thousands, or even millions of customers. When customer data is stolen, the company is likely to lose customers and face expensive lawsuits. Breaches involving 50 million records or more cost 100 times more than the data breach average.
Incident Response and Recovery
As soon as a breach is discovered, you must act immediately to minimize damage. Immediate data breach response activities can quickly add up and ongoing recovery efforts can last months. Incident response is a complex process that needs to be done right, often requiring organizations to hire an experienced incident response team.
Immediate requirements include:
- Quarantining the Threat: This can mean shutting down compromised hardware and software.
- Data analysis: Cybersecurity experts will analyze activity logs to find the cause of the breach and determine the extent of escalation.
- Eliminate Vulnerabilities: Upon detection of the root cause of the threat, it's essential to immediately take action to eliminate the vulnerability to avoid secondary attacks.
- Repair or Replace Infected Systems: It's common for network components and software to be damaged due to an attack. Taking care of damaged systems is critical to avoiding increased downtime costs.
- Improving Security: It's important to note that a successful breach represents a security failure. Eliminating one vulnerability isn't enough. You need tools in place to detect and respond to breaches in real-time to effectively protect your organization from another attack in the future.
For IT specialists who have seen the sheer volume of information that covers everyday network activity, it's likely not surprising that each step in your incident response procedure can take days, weeks, or even months. The costs of these tasks increase with the length of time required for completion as well as the level of damage that has occurred.
As pointed out in the Cost of a Data Breach report, the response system your organization has in place can have a major impact on your overall recovery costs. When automation and security AI are fully deployed, organizations paid up to $3.81 million less than those without it. Automated responses and the use of AI offer immediate incident response actions with fewer false positives than other systems. When a breach occurs, specific actions are immediately triggered to stop the attack and alert the proper personnel. Similarly, companies with a zero-trust strategy reduced the cost of a breach by $1.76 million. A fully mature zero-trust strategy adds another layer of security that requires verification from everyone trying to enter the network resulting in fewer successful breaches.
Lost Business
While many companies focus immediately on the cost of the ransom demand itself, the cost of lost business is likely to be the biggest cost of a data breach. When a data breach occurs, business is disrupted and your loyal customers recognize that their information is at risk. After the breach is contained, prospective customers are likely to consider your organization unworthy of their trust. As a result, lost business accounts for 38% of the total costs accrued by a data breach.
A data breach instantly creates negative news about a brand, which can stick in a prospective customer's mind longer than positive press. Studies show that 81% of consumers will stop engaging with a brand online following a data breach. The loss of customers affected by the breach could result in a significant and immediate blow to a business. Even the costs of lost business during downtime related to the attack have a significant impact on a company's bottom line.
Breach Notification
All states have legislation that requires notification of data breaches involving personal information. You must notify law enforcement, affected businesses, and affected individuals. In some cases, you may also need to contact major credit bureaus, the FTC, or state or federal law enforcement. Taking care of this level of information distribution in a timely manner can be costly.
The way you respond to a data breach will have a critical impact on the way consumers view your business moving forward. The notification costs typically included in data breach reports include:
- Emails, letters, outbound calls, or other notices to victims affected by the attack
- Determination of regulatory requirements
- Communication with regulators
- Engagement of outside experts
However, it fails to recognize the cost of addressing the public and announcing an effective response to the attack. Your notification process should ensure that affected parties are notified before news about the breach goes public. Anything less looks like you're withholding information and your business is no longer trustworthy.
Downtime
Time is money, and many companies run during all hours to maximize production. However, the effects of a cyberattack or even responding to a potential attack can force your business to come to a grinding halt. The biggest reason that companies pay a ransom is to avoid expensive downtime. The average downtime a company experiences after a ransomware attack is 21 days. While the primary objective of a data breach is data theft, many attackers now use stolen data to extort a ransom from the victim company. As a result, the downtime experienced from a data breach can mimic that of a ransomware attack.
The cost of downtime is more expensive than ever before, with 44% of firms reporting that hourly downtime costs exceed $1 million to over $5 million. 91% of organizations report that a single hour of downtime takes mission-critical infrastructure offline, resulting in lost business. Other costs of downtime include production decline, loss of sales, customer dissatisfaction, lost or damaged data, regulatory compliance fees, and restarting costs.
Compliance and Regulatory Fines
Most organizations are subject to strict guidelines regarding the protection of customer data. Of 25 cost factors identified by IBM, compliance failure increases cost more than any other factor. Organizations with high compliance failures paid an average of $2.3 million more for data breaches than those with low levels of compliance failures. Compliance-related costs may include fines, penalties, and lawsuits. Perhaps, more importantly, compliance failure can result in the loss of certification that allow your organization to complete certain business transactions. Reinstating the certifications can take several months in many cases.
Reputation Damage
A successful cyberattack or data breach has a major impact on your customers. From leaked personal data to the interruption of critical services provided by healthcare facilities or major infrastructure, the ramifications of an attack extend far beyond an organization. As a result, consumers are wary of interacting with an organization that failed to protect its customers. The best way to protect your company's reputation from the results of a data breach is a good offense that helps you avoid them. However, in the wake of a data breach, the organizational response will be the most effective tool to minimize reputation damage.
There is no way to completely avoid the loss of both loyal and potential customers after a data breach. This loss will cost your organization dearly. The response you'll need to take to reassure consumers your brand is trustworthy will cost as well. However, it can also be an investment that will help protect you from future attacks.
Legal Costs
When customer data is exposed or stolen, thousands of individuals could be affected. Depending on your industry, the effects of a data breach on customers could range from minimal to extremely severe. For instance, healthcare and financial services are heavily regulated and likely to pay more for compliance failures and breaches than companies in other industries. Additionally, the circumstances surrounding the breach can result in increased fines and lawsuits. For example, a company that fails to adequately respond to a known vulnerability is responsible for attacks that exploit the vulnerability.
Wondering how much legal fees can cost your company?
- Equifax paid $575 million in fines and settlements in 2019 after failing to inform customers of a breach.
- Uber paid $148 million in fines after 57 million user accounts were hacked in 2016 and the company paid the perpetrator $100,000 to keep the attack under wraps.
- Yahoo paid $85 million in fines and lawsuits after failing to disclose a 2013 security breach that affected its entire database of about 3 million accounts.
- Home Depot paid nearly $200 million after an estimated 56 million customers' personal and financial data was stolen and sold on the dark web. As a result of the breach, a massive number of fraudulent transactions were charged to customers' credit and debit cards.
- Capital One paid $80 million in fines after suffering a breach affecting 100 million people in the US and 6 million in Canada.
- Anthem Inc (the largest US health insurance company) was hacked, resulting in the theft of PII of 79 million customers. The company agreed to settle the resulting lawsuits for $115 million. Although, they claimed no customers were affected.
Time to Discovery
Often, today's cyberattacks are well-planned ventures that make the most of time spent inside a network. The longer a criminal lingers within your network, the more effective their attack can become. For instance, threat actors can gain higher levels of access or mine large amounts of data. The average time taken for organizations to contain data breaches in 2021 was 287 days. Breaches with a lifecycle of over 200 days had an average cost of $4.87 million compared to $3.61 million for breaches with a lifecycle of fewer than 200 days.
The more time a hacker has in your environment, the more access they can gain to different devices and accounts. When your network has integrated security features that provide automated responses to unusual behavior attacks are more likely to be recognized and stopped in a timely manner.
Loss of Business Connections
Practically all businesses depend on connections with other organizations for supplies, services, or additional business needs. The companies you connect with could potentially become a target of the hacker that exploits your network. Nearly two-thirds of cyberattack victims believe hackers gained access to their network through one of their suppliers or business partners. Since companies that have suffered an attack represent a potential threat, industry partners and other business relations could avoid your company after a breach.
- Recruiting employees can become difficult.
- Investors and shareholders may be hesitant to invest in a company or dump their existing stock.
- Vendors and suppliers may change financial terms, require higher minimum orders, or cease working with you.
- Industry partners could cut contact and business relations with you.
Employee Response
A cyberattack in-process is a highly stressful situation that can have a major impact on employee morale and in-office relationships. Furthermore, the impact of an attack on a business can also have an impact on the careers of the employees working in the organization. A drop in morale leads to lowered productivity and performance. The blame game that can arise during an attack can destroy employee relations and result in lasting hostility.
When an attack has a major long-term impact on a company, the costs can lead to layoffs, employee turnover, and difficulty recruiting new employees. After a ransomware attack, nearly 40% of organizations laid off staff, and 35% of companies suffered C-level resignations.
Avoiding the Costs of a Security Breach
The truth is, most organizations will eventually suffer a breach. Threat actors understand the difficulty of getting past modern network security tools. Instead of penetrating a network's defenses, hackers are much more likely to deceive users into providing a gateway. The most common initial attack vector for data breaches in 2021 utilized compromised credentials. Methods used include business email compromise, phishing, malicious insiders, and social engineering. Perimeter defense alone will never be enough to deter modern hackers. It's imperative for organizations to invest in an integrated defense system that recognizes the activities of threat actors within a network.
Beyond the expansive costs of a data breach, the 2021 Cost of a Data Breach Report revealed the ways new technology can help organizations limit the severity and elevated costs of a breach. For instance, the use of systems that utilize AI and automation cut the costs of a data breach by up to 80%. However, the tools that provide this level of security must be overseen by experienced cybersecurity professionals.
The cost and requirements of an on-prem SOC are far too expansive for most organizations to employ. The ongoing talent shortage of cybersecurity professionals makes it difficult for organizations to recruit a modest security team. Securing and optimizing highly technical security tools to use on-site can take months. For organizations that need immediate protection against modern cybersecurity dangers, cloud-based technology provided by an experienced cybersecurity company is the answer. If you're unsure about your organization's capability to handle a data breach, don't wait until after a catastrophic attack to take action. Take the BitLyft cybersecurity assessment to see ways that you can immediately increase your organization's cybersecurity posture and avoid the soaring costs of a data breach.
Sources:
1. https://www.ibm.com/security/data-breach
2. https://www.upguard.com/blog/cost-of-data-breach
3. https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/data-breach-response-guide-business
4. https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/blogs/ransomware-outlook-2022/
5. https://www.scmagazine.com/native/ransomware/the-state-of-ransomware-2022
6. https://www.cybereason.com/blog/report-ransomware-attacks-and-the-true-cost-to-business-2022
7. https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/ransom-payment-is-roughly-15-percent-of-the-total-cost-of-ransomware-attacks/
8. https://www.csoonline.com/article/3434601/what-is-the-cost-of-a-data-breach.html
9. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20191022005072/en/81-of-Consumers-Would-Stop-Engaging-with-a-Brand-Online-After-a-Data-Breach-Reports-Ping-Identity
10. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1275029/length-of-downtime-after-ransomware-attack/
11. https://techchannel.com/IT-Strategy/09/2021/cost-enterprise-downtime
12. https://revisionlegal.com/internet-law/data-breach/cost-of-data-breaches/
