Unleash Your Human Firewall: Mastering Employee Cybersecurity Training

 By
Emily Miller
·
8 minute read
By
Emily Miller
·
8 minute read
In a constantly evolving threat landscape where cybercriminals depend on highly evolved technology and even purchase ransomware as a service, there is one clear leader in the cause behind cybersecurity breaches. Nearly 90% of all data breaches are caused by human error. Does this mean that employees simply don't care about cybersecurity? Not likely. One in four employees identified as the responsible party loses their job within a year of the attack. It's a pretty harsh punishment to be indifferent about.
The reality is, sophisticated attacks that target humans are on the rise. In fact, 98% of cyberattacks involve some form of social engineering, and many attacks include 2 or more vectors to make the attack more convincing. Detections of multi-stage hybrid vishing attacks increased by nearly 550% between Q1 2021 to Q1 2022. While phishing is still the leading form of attack, social engineering attacks range from vishing (phone scams) and smishing (text scams) to business email compromise and quid pro quo attacks.
 When attacks are constantly evolving in both sophistication and number, employees are likely to be completely unaware of the different threats targeting your business. Attackers often convincingly impersonate legitimate business correspondence and frequently use internal methods to do so. It's impossible to threaten employees into recognizing the deluge of attacks, so how can you effectively decrease the risk of attack due to human error?
When attacks are constantly evolving in both sophistication and number, employees are likely to be completely unaware of the different threats targeting your business. Attackers often convincingly impersonate legitimate business correspondence and frequently use internal methods to do so. It's impossible to threaten employees into recognizing the deluge of attacks, so how can you effectively decrease the risk of attack due to human error?
Detailed cybersecurity training for all employees provides education about known and evolving attacks and how to avoid them. When you implement a comprehensive cybersecurity training program, you can unleash your human firewall by preparing employees to be a strong first line of defense against cyber threats. However, establishing effective cybersecurity training can be especially difficult for leaders of small and medium businesses (SMBs) without existing resources in place. This step-by-step guide provides 6 clear steps to help IT directors, IT managers, CISOs, and CIOs develop effective cybersecurity training for employees in SMBs.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Cybersecurity Landscape
Every business has a different risk landscape. Your industry, assets, size, and data collection and storage methods are all important features that contribute to your company's risk profile. By evaluating your risks and your current cybersecurity efforts, you can map out a plan for your cybersecurity training program. This three-step assessment will provide you with a comprehensive evaluation.
Identify Risks and Vulnerabilities
Your company's vulnerabilities are both industry and organization specific. To identify the risks that could make your company an attractive target, you'll need to determine potential network entry points and valuable information.
Every device that communicates with your network can be vulnerable to attack. Employees who use network devices for daily workflows are prime targets for social engineering attacks. Make a list of assets within your organizational network and the users who access them. Determine what types of data your business collects, stores, and shares. These are the areas that could make your organization vulnerable to attack. Effective cybersecurity training will center around protecting them.
Evaluate Current Cybersecurity Policies and Procedures
What are the existing measures you have in place to prevent attacks? Are you using a cybersecurity platform that identifies and responds to risks? Do you have an incident plan in place that outlines your employees' responsibilities? Do you have policies in place that require employees to use strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and safe data practices?
Once you've outlined your current cybersecurity practices, consider how effective they are against sophisticated attacks. Are you taking every precaution to protect your network?
Identify Areas where Employee Training is Needed
After evaluating your assets and current cybersecurity efforts, it's time to consider where employees are most likely to be targeted for attacks. From developing new policies to training employees about how attacks are carried out, you can develop a custom training plan to effectively educate your employees.
Step 2: Set Clear Training Objectives
Effective training requires a clear path that will align with your organizational goals. Remember, cybersecurity training is not a box to be checked on a list. It needs to be targeted, engaging, and achievable to supply employees with the education they need to ward off attacks. Begin by establishing measurable goals and objectives. What do you want the end result of training to achieve? How will you measure training success to ensure employees reach those goals? Once you establish your goals, detail them to align with your overall security strategy. Consider how your employees will be able to use the tactics they learn with your existing policies and tools.
With clear goals in place, you can define the topics employee training will cover. Topics should be based on your organization's unique risks so employees will learn to address realistic attacks they're most likely to encounter.
Cybersecurity Training Resources
There is no one size fits all approach to cybersecurity training. However, attempting to develop your own program from scratch can be intimidating. The following resources offer sample lessons and other free or inexpensive resources to help you get started.
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA): This page shares a variety of online lessons, exercises, and assessments for federal employees, critical infrastructure operators, and cybersecurity professionals.
- Infosec: This page includes free security training tools like quizzes, tests, training, and more to help businesses start cybersecurity training.
- ChatGPT: ChatGPT can use system training data as well as data collected from your network to generate reports about cybersecurity events. When combined with the system's NLP it can be used to develop highly accurate security awareness training materials.
- Cofense: A sample lesson of in-class simulation content
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services: Annual security awareness and role-based training
Step 3: Choose the Right Training Format
There are many different ways you can implement training for your employees. The format that you choose will need to work with employee schedules and the type of training most likely to engage your workforce. Cybersecurity training formats include classroom training, online training, video training, and simulation training. Sessions can be led by cybersecurity professionals or by your company leaders and IT team. Classroom and online training are usually considered to be the most engaging because instructors can be interactive and answer questions as they arise. Using simulation training in conjunction with other training methods can add to the learning experience and act as realistic testing to determine how much employees have learned.
Before settling on a training format, take the time to learn about each format and consider how the pros and cons of each will impact your employees. For example, is it practical for you to implement classroom training, or would online training be more convenient? Your employees' engagement rate is one of the most important factors, as engaged students are more likely to learn from the experience and participate in future training.
Step 4: Develop Engaging and Relevant Training Content
The content you include in your training sessions and exercises must be tailored to your organization's unique needs and risks to be relevant to your employees. While you'll want to use topics that relate to your industry and mimic realistic threats within your organization, topics will follow a general theme. Essential topics to cover, include:
- Cybersecurity basics
- Password management
- Email and phishing awareness
- Safe internet and social media use
- Malware and ransomware prevention
- Physical security
- Data protection and privacy
- Incident reporting and response
- Remote work and BYOD security
- Compliance and industry-specific regulations
It's crucial to remember the importance of engagement and applicable learning when developing topics. Cybersecurity is an ongoing process requiring continuous improvement. Engagement is key to actionable learning and retention. To promote active learning and engage employees, incorporate real-life examples, interactive activities, and exercises into training topics. As new skills are introduced, encourage employees to apply their newly learned cybersecurity skills to daily tasks in the workplace. Use the classroom and the workplace to connect training to real-life situations to help employees adopt practices they can use long-term.
Step 5: Establish a Culture of Cybersecurity Awareness
Cybersecurity is not a new tool or process that can be learned in a single training period. It's an evolving part of conducting modern business. In the same way that interconnected technology continues to change business operations, cyberattacks continue to evolve. As a result, cybersecurity awareness is a skill that must be acquired and retained by all employees in the modern workplace.
A culture of cybersecurity awareness is an environment where employees on all levels are aware of the dangers of modern and evolving cyberattacks and make protection against them a part of daily operations. Take a moment to consider how employees safely work around hazardous materials in the workplace. Industry-specific safety training is a part of how these companies operate. As a result, safety is embedded in the company culture and related workflows. By establishing a culture of cybersecurity, you can achieve the same level of safety against the damaging effects of cyberattacks.
It's important to note that developing a culture of cybersecurity can be challenging if you've had minimal security standards in the past. You should expect some resistance as employees are forced to learn new policies and procedures that impact their productivity.
These steps can help you successfully adopt and maintain a culture of cybersecurity in your organization.
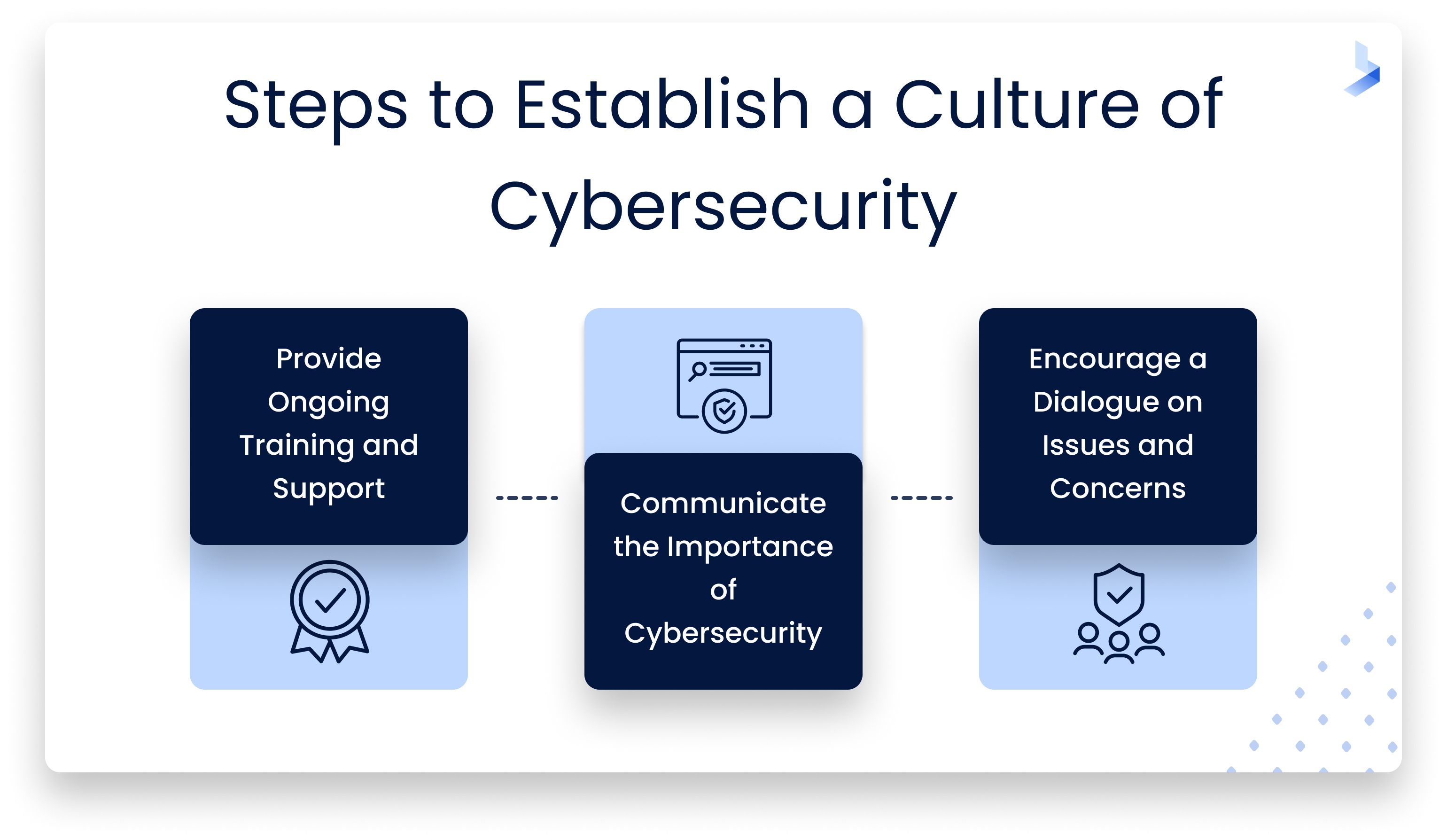
Provide Ongoing Training and Support
Cybersecurity training is a long-term investment, not a one-and-done goal to achieve. It's common for employees to face challenges during the implementation of secure practices that change daily workflows. How you support your employees during training and beyond will have a major impact on the level of resistance you're likely to encounter. When hurdles arise, be prepared to provide assistance, additional training, and support. Patience is key for the adoption of new policies. By providing ongoing support and training as needed, you can reinforce the importance of cybersecurity in the workplace and work through the kinks in your adoption plan.
Communicate the Importance of Cybersecurity Throughout the Organization
Effective cybersecurity is the responsibility of every employee from entry-level to the C-suite. Top-down support will be required to get buy-in from all employees. Remember, your employees can be your strongest defense against attacks or your weakest point of vulnerability. When company leaders and executives display a security-minded attitude, it will inspire employees throughout the organization to do the same.
Encourage an Open Dialogue on Cybersecurity Issues and Concerns
The cyber threat landscape evolves daily with new threats constantly emerging. Employees who stay current about top concerns and attack vectors are those who will help you maintain a secure network. Workplace conversations about cybersecurity issues help build a culture of cybersecurity awareness and bring attention to potential threats that can be avoided. Be prepared to answer questions, introduce new topics, and research when necessary to keep an open dialogue about effective cybersecurity and the effect it has on your business.
Step 6: Evaluate Training Effectiveness for Continuous Improvement
By now, you may feel like we've made it abundantly clear that cybersecurity is an evolving process. Still, it's a critical point that so many companies simply don't recognize. This step is where you bring the cyclic effect of cybersecurity training full circle for continued and ongoing growth. For cybersecurity training to be a valuable investment, you need to be able to measure the effects of your training program. Does employee testing yield high scores and impressive results? Can employees recognize sophisticated threats introduced in simulated exercises? Are cybersecurity best practices becoming a part of daily workflows? The answers to such questions can help you evaluate the effectiveness of your cybersecurity training program.
Your evaluation shouldn't begin and end with basic measurements and observations. Communicate with employees to learn about how new procedures affect workflows. Ask questions about your employees' confidence levels regarding their ability to avoid social engineering attacks and protect against common threats.
Use what you learn to update and refine training content to keep pace with evolving threats and industry best practices. Once you adopt a successful training program, it's easier to continue long-term training that keeps employees engaged.
Cybersecurity Training Unleashes Your Biggest Asset
Your employees are your organization's first line of defense against cyberattacks. Without an active and ongoing education, they won't have the resources to avoid sophisticated attacks targeted at your business. From communication to workflows and device use, cybersecurity is a crucial part of modern business operations. By investing in cybersecurity training for employees, you can unleash your human firewall for radically improved protection against the onslaught of social engineering attacks targeting businesses across all industries.
Effective cybersecurity is an ongoing process that will change and grow with your business. Cybersecurity training for employees is an investment with long-term ROI in the form of engaged and confident employees prepared to protect your network against cybercriminals.
Cybersecurity is a lot to manage on your own. Let BitLyft's managed detection and response services help extend your team. Contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive solutions tailored for SMBs.
