CMMC Compliance: An In-Depth Overview to Achieve Certification

 By
Jason Miller
·
17 minute read
By
Jason Miller
·
17 minute read
CMMC compliance is quickly becoming a vital part of doing business in the United States. Businesses have become aware of the stringent requirements in today's market. It's essential to understand CMMC compliance and how to become certified.
Without CMMC compliance, your business risks being shut out from lucrative contracts. In order to comply, your company must adhere to a set of guidelines. These ensure the security of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
In this guide, we will provide an in-depth overview of CMMC compliance. This includes requirements and valuable tools of the trade. We'll also discuss how to become certified and make your business compliant today!
Read on to delve deeper into the essence of CMMC. This will ensure a great future for your business.
What Is CMMC?
CMMC compliance is a new standard that was developed by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD). It was created to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) better.
The CMMC standard consists of 17 different maturity levels, each with specific requirements. Businesses must meet all 17 levels to be certified compliant.

The CMMC standard was created in response to growing concerns about the security of CUI. In recent years, there have been several high-profile data breaches that failed to protect CUI adequately.
The most notable example is the 2017 Equifax breach. This exposed the personal information of over 140 million people.
The DoD now requires all contractors who handle CUI to be certified compliant with CMMC. This includes businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large corporations.
| Related Reading: Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) 2.0: An Overview |
What Is the Department of Defense?
The Department of Defense is the federal agency responsible for the defense of the United States. This includes its armed forces, military history, and budget.
The purpose of this agency is to protect the American people from harm. This includes threats from other nations, terrorist organizations, and natural disasters.
Furthermore, the Department of Defense is responsible for the development and implementation of defense policy. This policy must be approved by the President and Congress.
The Department of Defense was established in 1789. It is the oldest federal agency in the United States.
The DoD has undergone many changes over the years, as it adapts to changing threats. The most recent change is the development of the CMMC standard.
This new standard was created in response to growing concerns about the security of CUI. In recent years, there have been several high-profile data breaches that failed to protect CUI adequately.
What Is Controlled Unclassified Information?
Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) is any information that requires security protections. This includes information that could be used to damage national security if it were released to the public.
CUI can come in many forms, such as:
Classified information: This is information that has been determined by the government to require security protection. It cannot be released to the public without authorization.
Sensitive information: This is information that is not classified but could be used to damage national security if it were released.
Proprietary information: This is information that is owned by a private company and considered confidential.
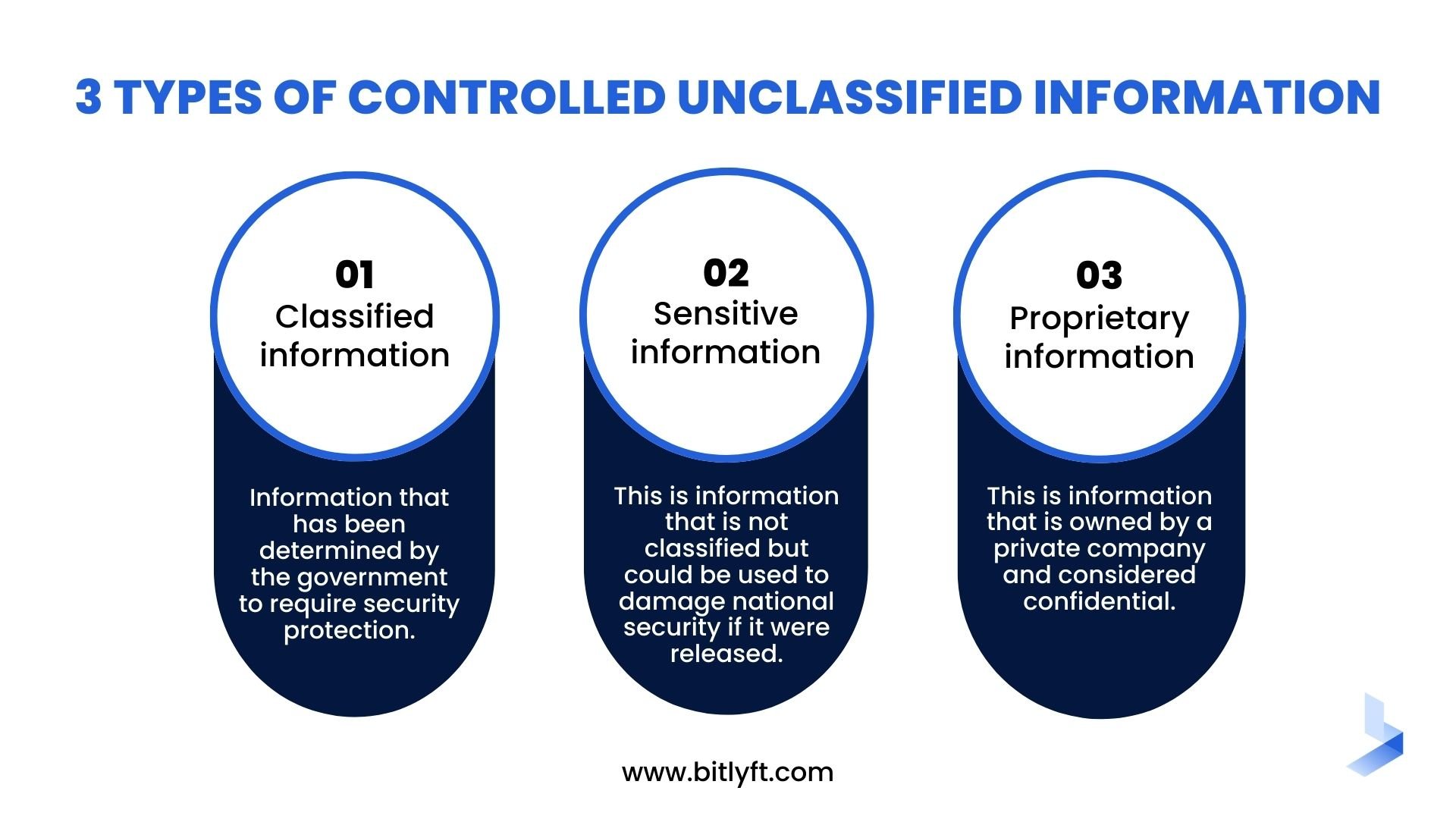
In other words, CUI is any information that should not be made public. This includes information that could harm national security or the financial interests of a private company.
The CMMC standard was created to protect CUI better. It requires businesses to meet 17 different maturity levels, each with specific requirements.
What Are the Greatest Risks to Controlled Unclassified Information?
There are many risks to CUI. The most common risks include:
Theft: CUI can be stolen by anyone with physical access to it. This includes employees, contractors, and outsiders.
Espionage: CUI can be sold or given to another country for their use.
Sabotage: CUI can be destroyed to prevent its use by the government or a private company.
Cyber attacks: CUI can be accessed and stolen through cyber attacks, such as hacking.
Accidents: This is when CUI is released accidentally, without authorization.
These are just some of the risks that CUI faces. The CMMC standard was created to protect against all of these risks and more.
Why Is CMMC Important?
The simple answer is that CMMC compliance is essential because the DoD requires it. If your business wants to contract with the DoD, you must be certified compliant.
But CMMC compliance is about more than just meeting a contractual requirement. It's also about protecting your business and ensuring the security of CUI.
Data breaches can be costly, damaging your business's reputation and leading to financial losses.
In some cases, data breaches can even result in legal action against your business. by implementing the requirements of CMMC, you can help protect your business from these risks.
What Are the Benefits of CMMC Certification?
There are several benefits of CMMC certification, including:
- By achieving compliance with CMMC, businesses will improve their overall security posture.
- Certified businesses will render trust with customers knowing they have protected sensitive information.
- With the DoD mandating CMMC for all contractors, businesses that are certified will have a competitive edge over others.
Achieving compliance with CMMC can be a daunting task. It is essential for businesses that want to work with the DoD. By following our in-depth guide, you can ensure your business is prepared for the certification process.
CMMC 1.0 vs CMMC 2.0
There are only three current CMMC levels, which were determined by eliminating two out of the original five. These include Level 2 (CM/sub-criteria) and 4 (Multi criteria).
The new certification requires that every company leader undertake an annual self-assessment.
The 17 basic cyber hygiene practices are not changed with this change. It does bring them one step closer to meeting the government's standards for security awareness.
The Secretary of Defense has announced that they will be removing 20 controls from Level 3.
This leaves contractors only implementing 110 out hips in NIST 800-171. They also identify prioritized acquisitions for an independent third-party assessment against new requirements.
This is done through the Office of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment in the United States.
The final level of the framework is expected to replace CMMC levels 4 and 5 with government-led assessments. This will be done according to SP 800 172 standards and other applicable regulations. For instance, those set by NIST or supplement DFARS (Department Of Defense FAR Supplement).
Brief History of CMMC
In 2002, Cybersecurity Research and Development Act authorized appropriations to National Science Foundation. It was done to create new programs and increase funding for certain current ones.
This led to NIST's work in security research and requirements set forth by maturing model certification framework. Also known today as Federal Information Security Management Act or FISMA.
FISMA, a project launched in 2003 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) resulted in several publication. These include FIPS 199 and 200.
Then NIST Special Publications 800-53 through 800-6 were released between 2004-2010. These all contain guidance on safeguarding unclassified information
In 2011 Executive Order 13556 was signed, creating standards for labeling data across government organizations under certain circumstances. The Defense Industrial Base DIB is known as the political science in reference to government industrial assets of importance to equipment production in a country's armed forces.
This executive order also led to proposed rule 7000 pertaining specifically to Fundamental Research when it comes into contact outside its original classification.
More Recent Years
In 2013, the Department of Defense (DoD) issued DFARS 252-204 7000 Rule, which requires protection-sensitive data on nonfederal systems.
This goes into effect after 2016 when clause 7012 comes into development. Thus, requiring all contract holders to assess their security capabilities.
Also, to provide proof at start-up or annual intervals through self-assessment according to NIST SP 800-171 standard.
In 2019, the Department of Defense announced that it would institute a new certification program to help contractors manage their cybersecurity requirements.
The first step in this process is called CMMC. This stands for Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification CMMC.
It requires all those who work with information technologies (IT) systems on behalf of or perhaps even against federal government agencies like NASA must assess how prepared these companies are for security.
In 2020, the General Services Administration released a Request for Proposal that all government contractors should prepare to meet CMMC requirements.
The Department of Defense announced its new version on November 4th, 2021, designed to streamline its original ones.
It eliminates some outdated provisions while effortlessly adding others. As long you are compliant with one set or both sets (or anything else), then the business can continue without any hiccups whatsoever!
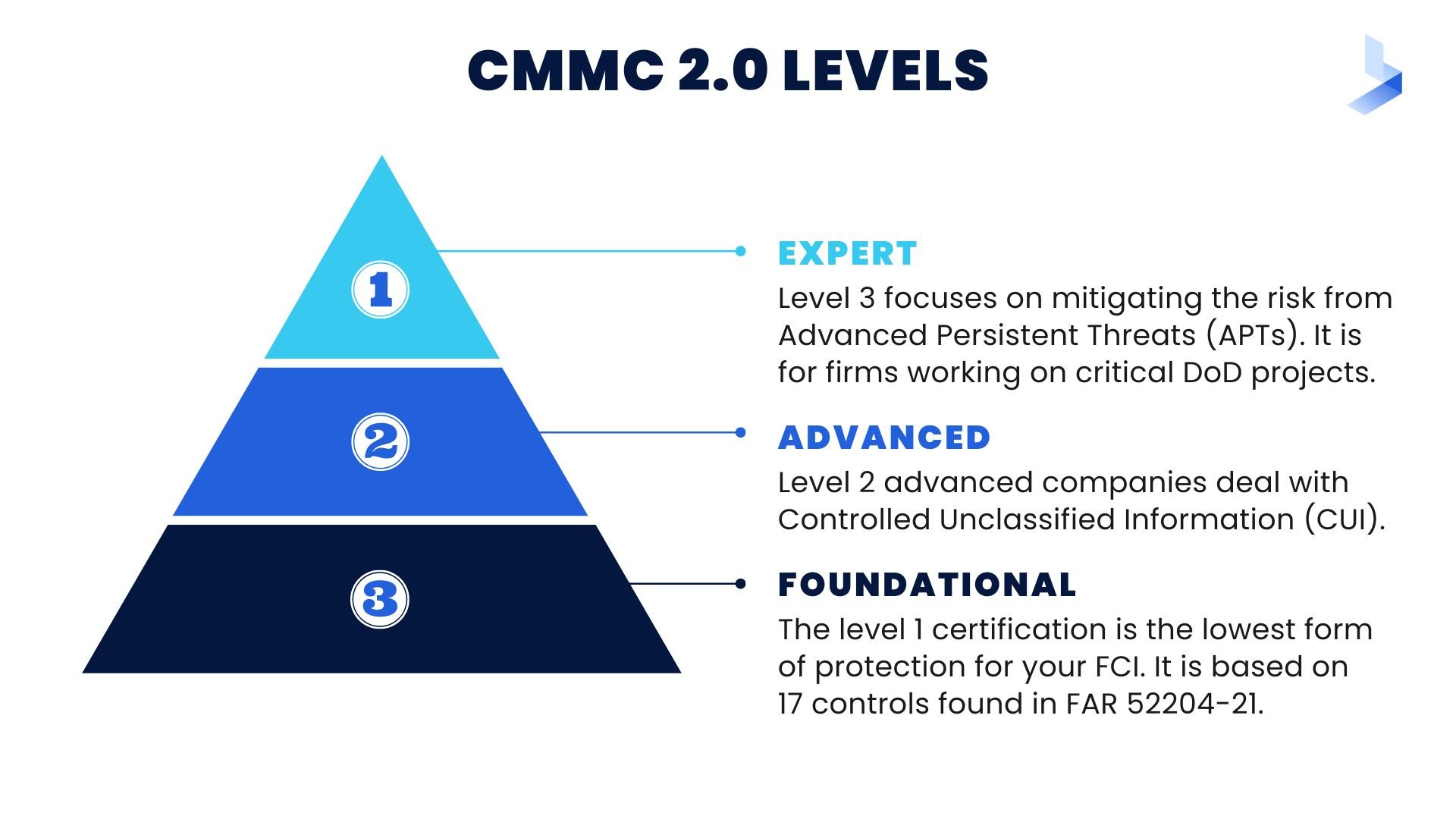
What Are Some of the Requirements/Practices for CMMC Level 1: Foundational?
Level 1 of the organization C3PAO certification requires organizations to perform basic cybersecurity practices. They may be able to do these in an ad-hoc manner without relying on documentation. They are allowed reach level 2 through annual self-assessment.
Still, they must first pass a test covering 48 CFR Parts 52.204-21. This includes proper safeguarding requirements for sensitive personal information under control (FCI).
As you can see, the requirements for CMMC program are not particularly demanding. Many businesses are already doing most of these things to protect their data.
Level 1 of the certification process is required for DoD contractors and subcontractors. Specifically, those that handle Federal Contract Information (FCI), or “Information not for public." This includes all information provided by the contract to develop products/services.
To achieve CMMC Level compliance, your business will need to develop and document policies. As well as procedures for each of the requirements. You will also need to train your employees on these policies and procedures.
What Are Some of the Requirements/Practices for CMMC Level 2: Advanced?
Level 2 requires organizations to document their processes in a way that can be repeated by those who want or need them.
This documentation is essential because users must know how these steps work. It also requires them to be available for quick reference if needed during an emergency where time isn't on your side!
The Level 2 maturity level includes all 14 domains from SP 800-171 and 110 controls. These are unique specifically for CMMC 1.02 plus 20 eliminated items at Level 3&4.
The requirements for compliance differ on the CUI data criticality to national security.
Organizations with priorities with higher levels of sensitivity must pass a CMMC third party assessment. While those without any particular sensitivities can conduct an annual self-check every year. The frequency of these assessments will increase as the level goes up.
CMMC level 2 is for DoD contractors and subcontractors. For those that handle the same type of controlled unclassified information, they must meet level two compliance.
A lower CMC may apply if only specific data will flow down from your prime contract, or even just one piece. In particular, can be considered sensitive enough to require this level instead!
As you can see, the requirements for CMMC Level are more demanding than those for Level 1. To achieve compliance, your business will need to have procedures and controls in place for each of the requirements. You will also need to train your employees on these procedures and rules.
What Are Some of the Requirements/Practices for CMMC Level 3: Expert?
At CMMC level 3, an organization is required to establish and maintain a plan. It must detail how it will manage activities needed for implementing its cyber security.
This includes information on specific topics like goals or projects. Starting with NIST SP 800-171 (good cybersecurity practices). As well as 20 additional models at this stage of maturity.
These can include securing data assets through encryption algorithms. All while protecting against advanced persistent threats. It also involves training employees who handle sensitive material.
DFARS clause 252.204-7012 still applies. Thus, adding more requirements beyond NIST SP 800171, such as reporting security incidents.
The level 3 CMMC is applicable for companies that handle CUI on DoD programs with the highest priority. It’s comparable to Level 5 though there are some differences between them too.
This is mainly due to their varying lengths (110 vs 65). It's worth noting, however. This new version from 2020 onward has already indicated specific controls will be based on NIST SP 800-171B.
The most significant change that sets level three apart is the inclusion of a plan. As mentioned, it details activities needed for its cyber security practices to be managed.
How to Determine the Level of Compliance for You?
The first step is identifying the Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) in your environment. You must understand how it flows through your company. You will need to know what systems handle this data, where it is stored, and how it is transmitted.
Once you have a good understanding of your CUI landscape, you can begin to map out plans. You will come to know which CMMC level is appropriate for your company.
This is done by taking a self-assessment of your current cybersecurity posture. Then you compare it to the requirements of each level.
Take a look at these types of CMMC domains and their capabilities to understand what you need to consider.
Access Control
The security domain that covers identification, authentication, and authorization.
Also, includes subjects, objects, and the relationships between them.
Asset Management
The security domain that includes physical and logical assets.
This covers identification, classification, handling, storage, and disposal.
Awareness And Training
The security domain that encompasses employee training on cybersecurity risks and procedures.
This involves educating staff on topics such as social engineering and phishing scams.
Audit And Accountability
The security domain that keeps track of user activity via logs or other records to ensure compliance with policies.
This also covers identifying and responding to incidents in a timely manner.
Configuration Management
The security domain that covers maintaining an inventory of hardware, software, networks, configurations, etc.
Other aspects of this domain include change control and status accounting.
Identification And Authentication (I&A)
Also known as "authentication", this is the process of verifying someone's identity.
This CMMC domain is critical for ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to CUI.
Incident Response
The security domain that covers detecting, responding to, and recovering from a cybersecurity incident.
Response is just as important as prevention when it comes to cybersecurity.
Maintenance
The security domain that covers preventative measures taken to ensure systems are functioning properly.
Without maintenance, systems are more susceptible to vulnerabilities and attacks.
Media Protection
The security domain that encompasses the physical and logical safeguarding of removable media (e.g., USB drives).
Protection of media is an organizational responsibility, not just an individual one.
Physical and Environmental Protection
The security domain that safeguards people and systems from physical threats like fire, flooding.
These aspects are often dismissively called "the basics". Yet, they are critical for security.
Recovery Planning
The security domain that includes planning for how an organization will recover from a disaster or incident.
Disasters do occur, and being prepared can mean the difference between a minor setback and a major one.
Risk Management Framework (RMF)
Also known as "risk management", this is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks.
Prevention is the best medicine for compliance, but being prepared for incidents is also important.
Security Assessment And Authorization (SA&A)
This is the process of assessing and authorizing information systems.
It's important to assess all systems, not just those that handle CUI of your organization. All from the way you develop software to the way you handle customer data.
Situational Awareness
The security domain encompasses monitoring for threats and vulnerabilities. As well as taking action to protect assets.
This goes hand in hand with prevention. Thus, being aware of potential threats can help you avoid them altogether.
System And Communications Protection
The security domain that covers communication protocols and system security controls like encryption.
Without certain security protocols in place, communications can be intercepted and systems can be compromised.
System And Information Integrity
The security domain that ensures data accuracy and completeness. As well as protection from unauthorized modification or destruction.
Another important aspect is ensuring data retains versioning control throughout its lifecycle.
Data integrity is essential for maintaining the trust of your customers and partners.
How Does CMMC Differ From NIST 800-171?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-171 is a set of security requirements. They are for non-federal information systems that handle CUI. It was released in 2015 and updated in 2020.
CMMC builds on NIST 800-171 by adding new requirements and increasing the level of rigor for each condition. For example, NIST 800-171 requires companies to have a plan for managing their cybersecurity program. All while CMMC Level III requires companies to have an actual program in place.
In addition, CMMC introduces new concepts not found in NIST 800-171. For instance, supply chain risk management and situational awareness. Also, while NIST 800-171 is focused on protecting CUI, CMMC is designed to preserve FCI and CUI.
Finally, it's important to remember that CMMC is not just a checklist of things to do. It is a journey that starts with understanding your risks. It's about continuously improving your cybersecurity program.
| Related Reading: Comparing NIST and CMMC |
What Are Some Valuable Tools of the Trade?
There are several valuable tools that businesses can use to help with CMMC compliance, including:
Policy management software can help businesses develop, manage, and enforce security policies. Also, it can automate compliance reporting.
Vulnerability management software can help businesses scan systems for vulnerabilities and provide remediation guidance.
Compliance management software can help businesses track compliance with various regulations, including CMMC. In addition, it can automate compliance reporting.
Security information and event management (SIEM) software can help businesses. They do so by collecting and analyzing data from various security devices and systems. This can provide insights into potential threats and incidents.

Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) can help businesses. In their case, they detect and prevent attacks by identifying suspicious activity.
Training programs can help businesses educate their employees on the importance of compliance. They also provide the proper way to protect sensitive information.
How to Become Certified In CMMC Compliance?
The first step to becoming certified is to find a registered certification body.
There are currently only four RCBs authorized by the Department of Defense: ANSI, CERT, CIS, and EY. Also, check that the RCB is on the list of approved organizations. This is published by the Department of Defense.
Once you have selected an RCB, you must apply for evaluation. The evaluation process includes a review of your policies and procedures. It also covers well as on-site audits at your facilities.
.jpg?width=1024&height=768&name=Five%20Steps%20to%20CMMC%202.0%20Certification%20(1).jpg)
In addition, you will need to submit documentation demonstrating compliance with the CMMC.
After you have completed the evaluation process, you will receive a certificate of level of compliance. You can then use this certificate to bid on contracts. This is if they require CMMC certification.
As you can see, there is a lot that goes into achieving CMMC compliance. However, the effort is well worth it to protect your business.
Issues That Might Prevent CMMC Certification
There are a few potential issues that could prevent your business from becoming CMMC certified. These include:
Not understanding the requirements: The CMMC standard is complex, and it can be difficult to understand all of the requirements. Also, the requirements can change over time.
Not having enough time: It can take a significant amount of time and effort to achieve compliance.
Not having enough resources: Compliance with CMMC requires investment in people, processes, and technology. In addition, it can be costly to achieve and maintain compliance.
Not having the right people: Your business needs employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement CMMC.
These are just some of the potential obstacles you might face when trying to become CMMC certified. However, by following our guide, you can overcome these challenges and ensure your business is compliant.
Common Mistakes Made With CMMC Compliance
One common mistake businesses make failing to train their employees on the requirements properly.
Another common mistake is not having a clear understanding of the requirements themselves. This can lead to businesses implementing controls that are not required or failing to implement rules that are needed.
There's also the challenge of maintaining compliance over time. This is why it's essential to have a plan in place for how you will maintain compliance going forward.
Besides the initial effort of becoming compliant, you will need to periodically review your policies and procedures and update them as needed.
You will also need to keep up with changes to the CMMC requirements themselves. The Department of Defense is always working to improve the CMMC, so it's important to stay up-to-date on the latest version.
What Are the Penalties for Non-Compliance?
The penalties for non-compliance with CMMC can be severe. The Department of Defense can withhold payments. They can terminate contracts and even impose criminal penalties.
Furthermore, the Department of Defense is not the only organization that can penalize businesses. Many other government agencies and private companies now require CMMC certification.
In addition, businesses that are not compliant may be barred from bidding on future contracts. This is why it's essential to take compliance seriously.
It's critical to ensure you are taking the necessary steps to meet the requirements.
As a final note on penalization, it's essential to keep in mind that the Department of Defense can choose not to penalize a business. This is if it is working diligently to become compliant.
This is why it's essential to start the compliance process as soon as possible. You must have a plan in place for how you will achieve and maintain compliance over time.
How to Enable And Optimize CMMC Compliance Over the Long-Term?
The best way to enable and optimize CMMC compliance over the long-term is to have a clear understanding of the requirements. This is done to put in place policies and procedures that will ensure compliance.
In addition, it's essential to train your employees on the requirements and what they need to do to help meet them.
Finally, you need to have a plan in place for how you will maintain compliance over time. This includes periodically reviewing your policies and procedures and updating them as needed.
Implement A Platform That Securely Transmits CUI
The first step in ensuring CMMC compliance is to have a platform in place that will securely transmit CUI. There are several different platforms available, so it's essential to choose one that meets your specific needs.
Once you have chosen a platform, you must ensure it is properly configured. This includes setting up user accounts, establishing access controls, and configuring security settings.
It's also essential to ensure that the platform is regularly updated with the latest security patches. This will help to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
Engage An Extensive System Security Play
Another critical element of CMMC compliance is implementing an extensive system security playbook. This should include all the policies and procedures you need to ensure compliance.
The playbook should be tailored to your specific business and should be regularly updated as needed. It's also essential to train your employees on the contents of the playbook so they know what is expected of them.
Also, make sure you have a plan in place for how you will respond to security incidents. This should include procedures for identifying, reporting and responding to incidents.
Consider A Consulting Partner for CMMC
If you are struggling to meet the requirements of CMMC, you may want to consider working with a consulting partner.
They can assist in developing compliance policies and procedures. They also help with implementing security controls and training your employees.
They can also help you to assess your current level of compliance and develop a plan for how you can improve. Working with a consultant can be an invaluable step in ensuring CMMC compliance.
Some of their core values should be:
- Making security everyone's responsibility
- Automating repetitive tasks
- Applying security at every stage of the development process
- Continuously monitoring and improving systems
These are just a few things you need to do to ensure CMMC compliance. By following these steps, you can help to protect your business. You also ensure you can bid on future contracts.
The Future of CMMC
The future of CMMC is looking bright. The Department of Defense is committed to its implementation and has stated it will continue to evolve.
This means that businesses need to be prepared for changes in requirements. They must also be prepared to train their employees on the latest requirements.
In greater detail, businesses need to:
- Understand that CMMC is an evolving standard
- Be prepared for changes in the requirements
- Train their employees on the latest requirements
- Have a plan in place for how they will maintain compliance over time.
To be more specific, businesses need to understand that the CMMC is not a static document. The DoD is constantly reviewing it and making changes as they see fit.
They have also said that they will continue to add new requirements in the future. This means that businesses need to be prepared for changes in conditions.
They must also be prepared to train their employees on the latest requirements. This includes periodically reviewing your policies and procedures and updating them as needed.
Finally, businesses need to have a plan in place for how they will maintain compliance over time. This includes regularly assessing their compliance levels and taking steps to improve.
What Role Does SIEM Play In CMMC?
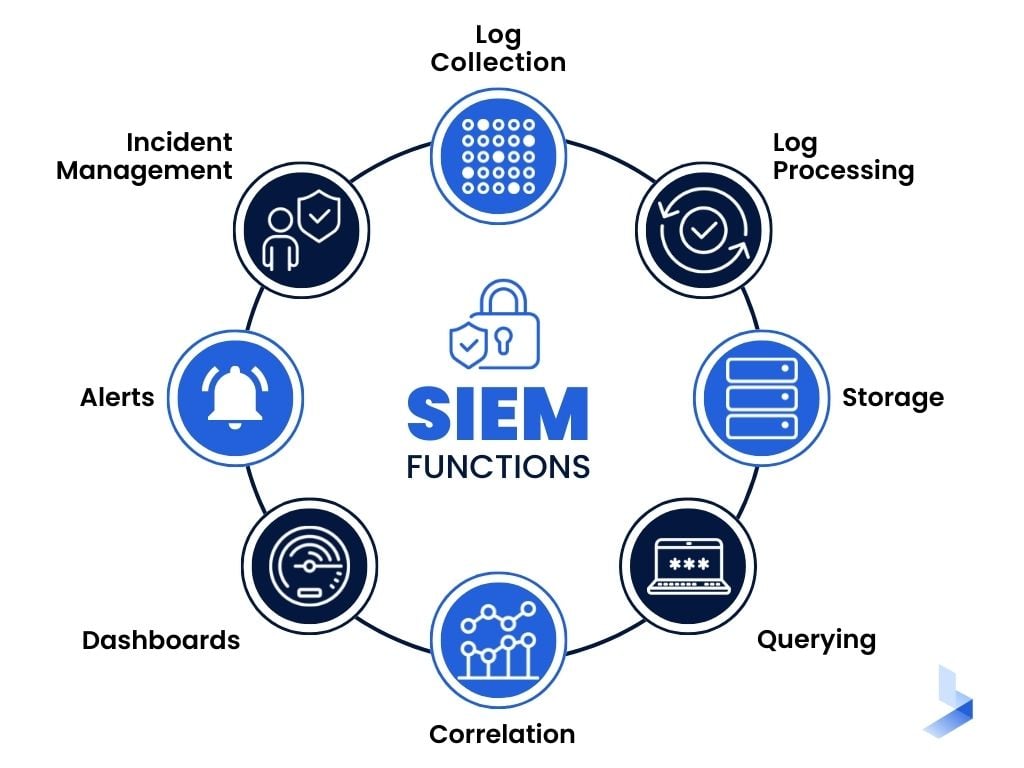
As you work to ensure CMMC compliance, you may be wondering what role SIEM plays. SIEM is a critical tool that can help you to meet the requirements of CMMC.
SIEM stands for security information and event management. It is a platform that collects and analyzes data from your network. This data can include everything from user activity to system logs.
SIEM can be used to detect potential threats and vulnerabilities. It can also be used to monitor compliance with policies and procedures.
There are many different SIEM platforms available on the market. You will need platforms, establishing access controls, and configuring security settings. It's also essential to ensure that the platform is regularly updated and that you have a plan in place for how you will respond to incidents.
By using SIEM, you can help to ensure CMMC compliance. This is because SIEM provides you with the ability to track, record, and monitor all activity on your network in real-time.
This means that you can quickly identify and respond to any potential threats or vulnerabilities. In addition, SIEM can also help you to automate many of the compliance-related tasks, such as patch management and log review.
What Role Does MDR/XDR Play In CMMC?
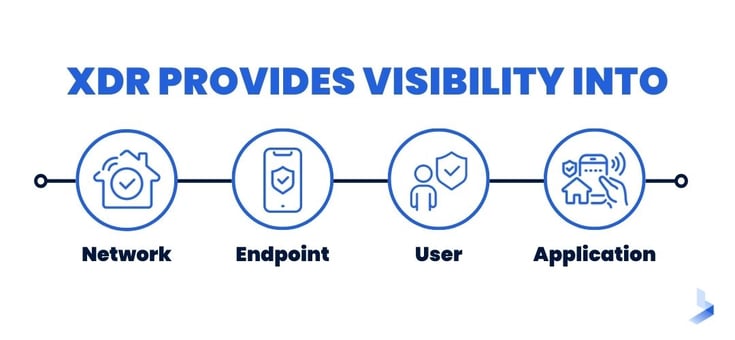
MDR/XDR is another tool that can be used to ensure CMMC compliance. MDR stands for managed detection and response. XDR stands for extended detection and response.
MDR/XDR platforms are designed to provide visibility into your network and help you to identify potential threats. They can also be used to monitor compliance with policies and procedures.
MDR/XDR platforms typically include a SIEM platform as well as other security tools. This allows them to provide comprehensive protection for your network.
When selecting an MDR/XDR platform, it's important to choose one that is designed for your specific needs. You should also make sure that the platform is regularly updated and that you have a plan in place for how you will respond to incidents.
By using MDR/XDR, you can help to ensure CMMC compliance. This is because it provides visibility into your network and helps you to identify potential threats. It can also be used to monitor compliance with policies and procedures.
What Role Does Log Management Play In CMMC?
Log management is another tool that can be used to ensure CMMC compliance. Log management platforms are designed to collect and store data from your network. This data can include everything from user activity to system logs.
Log management platforms can be used to detect potential threats and vulnerabilities. They can also be used to monitor compliance with policies and procedures.
When selecting a log management platform, it's important to choose one that is designed for your specific needs. You should also make sure that the platform is regularly updated and that you have a plan in place for how you will respond to incidents.
By using log management, you can help to ensure CMMC compliance. This is because you will have a complete and accurate record of all activity on your network.
This includes who did what, when they did it, and from where they did it. Having this information can help you to quickly identify any potential issues and take corrective action.
The Importance of a Powerful Vulnerability Scanner
A vulnerability scanner is a tool that can be used to identify potential vulnerabilities in your network. Vulnerability scanners can be used to detect weak passwords, open ports, and unpatched systems.
Vulnerability scanners are an essential part of any security program. They can help you to quickly identify and fix potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
When selecting a vulnerability scanner, it's important to choose one that is designed for your specific needs. You should also make sure that the platform is regularly updated. You must have a plan in place for how you will respond to incidents.
By using a vulnerability scanner, you can help to ensure CMMC compliance. This is because you will be able to identify potential vulnerabilities in your network.
Having this information can help you to quickly take corrective action. It will prevent attackers from exploiting these vulnerabilities.
CMMC Compliance Done Right
As you can see, CMMC compliance is vital for businesses that work with the Department of Defense. There are severe penalties for non-compliance. Thus, it's essential to take the necessary steps to meet the requirements.
However, the effort is well worth it to protect your business. As a consequence, the sensitive information it handles.
Complying with CMMC requirements can help your business run more smoothly. It will also protect your data from threats.
If you need help getting started with CMMC compliance, we can assist you. We offer a variety of services to help businesses meet their requirements. This includes certification assistance, training, and gap analysis.
