Cost-Saving Secrets: 10 Ways MDR Security Boosts Your Budget

 By
Emily Miller
·
11 minute read
By
Emily Miller
·
11 minute read
We can't afford cybersecurity. It's a common statement issued by decision-makers in companies large and small. The truth is, in today's cyberthreat landscape, no business can afford not to invest in comprehensive cybersecurity.
Unfortunately, even when you know the astronomical costs of a breach or ransomware attack, it doesn't mean that the money for an effective cybersecurity solution will magically appear in an already strained budget. As a result, companies often depend on minimal solutions that focus on compliance and only address part of the problem. This "wait and hope for the best" approach is usually supplemented by investments in miscellaneous cybersecurity tools on an as-required basis.
Budgeting for minimal-cost tools on an as-needed basis usually backfires in multiple ways. Internal teams end up with a large collection of mismatched security tools that require optimization and oversight. Even worse, if these tools aren't deployed on an integral platform, they can interrupt the performance of one another, causing decreased performance. As a result, organizations face reduced success in reaching cybersecurity goals and networks often have critical vulnerabilities.
Managed detection and response (MDR) provides businesses with a complete end-to-end cybersecurity solution customized to meet industry risks and unique organizational security posture needs. It also can save your organization money compared to traditional cybersecurity tools and services. Wondering how MDR security can actually help your company save money on cybersecurity? Consider these costs that will be decreased or eliminated with the use of a quality MDR solution.
1. Salary for Cybersecurity Professionals
In theory, an on-prem SOC is the most effective way to secure your organization's network. Yet, employing and maintaining a full cybersecurity staff is an expensive endeavor for any business. These are the average yearly salaries of cybersecurity team members.
- Analyst: $53K-$116K
- Engineer: $73K-$130K
- Director: $105K-$198K
- CISO: $176K-$263K
- CIO: $100K-$263K
Most companies require as many as four security analysts and engineers to effectively run security operations, making the average cost for yearly cybersecurity staff salary $739,000-$1,708,000.

Unfortunately, these estimates don't include the cost of 24/7 monitoring and employee benefits. It's common for cybersecurity professionals to work long hours, with over half of cybersecurity professionals working more than 40 hours each week and some working up to 90. Yet, even with a full team working a top number of hours, you'd likely need to double your cybersecurity headcount to achieve 24/7 security oversight and response capabilities.
Along with your team's salary and benefit requirements, recruitment is a critical cost that can be easily overlooked when calculating the salary of a full-time cybersecurity staff. Over two-thirds (67%) of security professionals say they don't have enough talent on their team. With $465,000 cybersecurity workforce roles unfilled in the US alone, recruitment is fiercely competitive, increasing the cost and time spent by organizations seeking talent.
2. Cybersecurity Tools
On average, organizations employ 29 different cybersecurity tools. Such tools can range from a typical firewall to complex software designed to carry out multiple security tasks. Business organizational networks continually grow and change for a variety of reasons including company growth and new workforce requirements. The cyberthreat landscape is continually growing as well. Because of this ongoing evolution, businesses must constantly upgrade cybersecurity tools to maintain an effective cybersecurity posture. These investments don't come cheap.
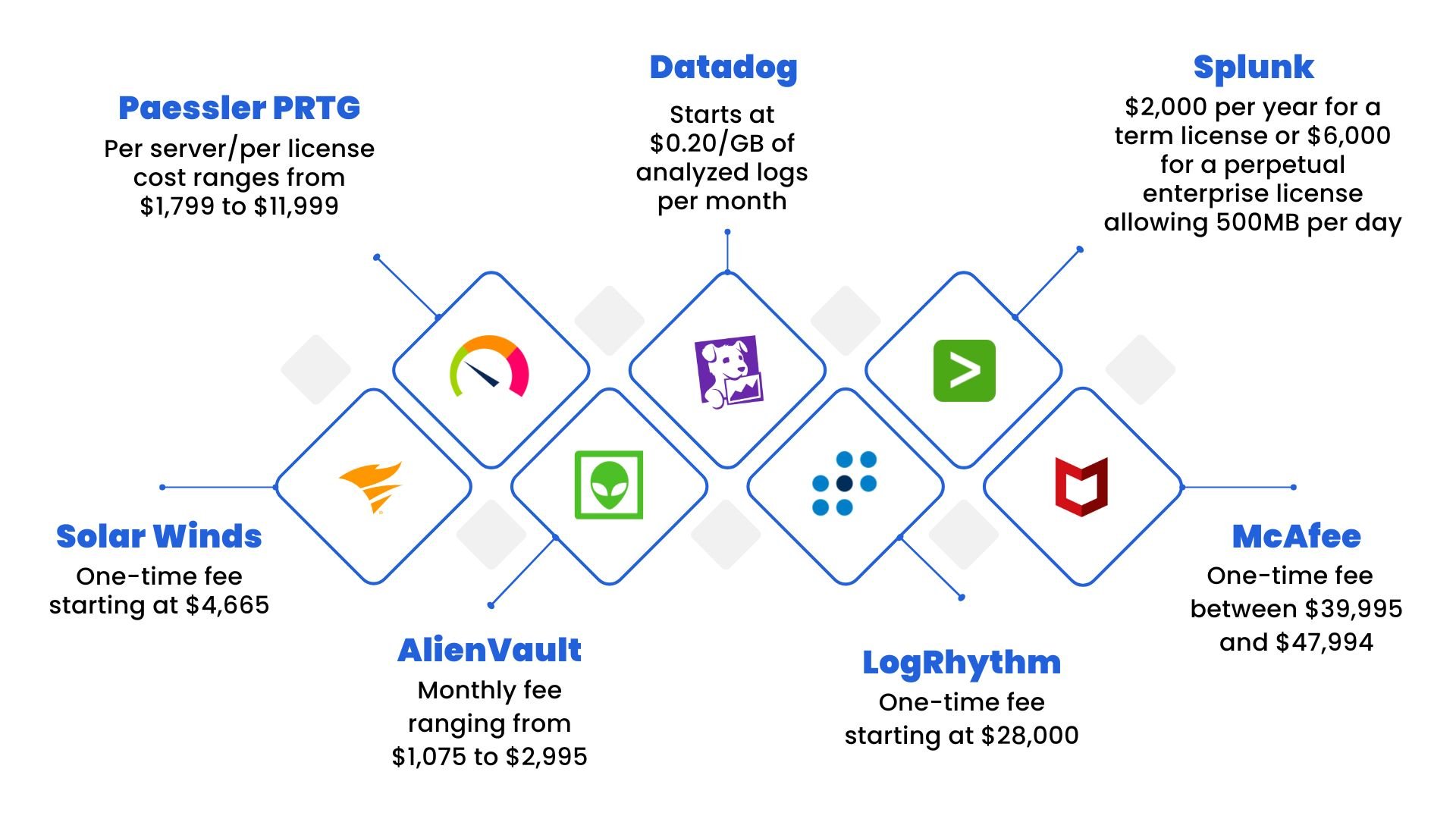
 For example, SIEM is a pivotal part of any cybersecurity system. When properly optimized and run by experienced professionals, the software provides storage, analysis, reporting, real-time monitoring, correlation, and notifications of and from network log data. SIEM tool prices range from a single fee to per-server, per-license fees, or fees based on amounts of logged data. An exploration of the cost of SIEM tools reveals a considerable investment.
For example, SIEM is a pivotal part of any cybersecurity system. When properly optimized and run by experienced professionals, the software provides storage, analysis, reporting, real-time monitoring, correlation, and notifications of and from network log data. SIEM tool prices range from a single fee to per-server, per-license fees, or fees based on amounts of logged data. An exploration of the cost of SIEM tools reveals a considerable investment.
- SolarWinds: One-time fee starting at $4,665
- Paessler PRTG: Per server/per license cost ranges from $1,799 to $11,999
- Datadog: security price monitoring starts and $0.20 per GB of analyzed logs per month
- Splunk: $2,000 per year for a term license or $6,000 for a perpetual enterprise license allowing 500MB per day
- McAfee: One-time fee $39,995–$47,994
- LogRhythm: One-time fee starting at $28,000
- AlienVault: Monthly fee ranging from $1,075–$2,995
Considering that SIEM is a single tool in your 29-piece cybersecurity toolbox, tool costs can quickly eat up your cybersecurity budget. Even worse, these tools can be rendered ineffective without the funds to cover the cost of implementation, training, staffing, and maintenance costs. Depending on the tools you choose, you may also be facing additional costs for hardware and infrastructure that can exceed the costs of the tools themselves.
3. Initial Optimization and Time to Value
Cybersecurity tools and systems are not out-of-the-box solutions that magically solve security issues upon deployment. While tools that utilize machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) can accomplish tasks that humans can't complete alone, they are tools designed to be used by professionals.
Modern cybersecurity solutions that collect and parse mass amounts of data, recognize suspicious activity, and launch automated response activities must be optimized to perform properly. Upon purchasing a new tool or system, your team will need to integrate the new software with existing solutions, set a baseline of use cases, and configure alerts.
Full optimization of cybersecurity tools that ingest and analyze data requires your team to identify and group data, weed out unimportant data and unknowns, conduct tests, provide feedback, and configure system reactions to alerts. As the number of log sources and endpoints your business needs to integrate grows, the time and effort spent integrating and optimizing tools increases. This is a process that could take weeks or even months to complete.
Furthermore, if you don't have dedicated cybersecurity specialists familiar with the equipment, you'll likely need to pay a third-party team to optimize software and tools for effective results. Conversely, an experienced MDR provider will take about 25% of the time an organization will take on its own to optimize tools and provide full value.

4. Training Expenses
Cybercriminals are innovative, determined, and always learning new ways to breach systems for monetary gain. Technology is advancing faster than ever before. Cybersecurity is not a stagnant profession with a single set of rules that lasts the span of a career. Cybersecurity professionals like security analysts and engineers must participate in ongoing training and upskilling programs to understand new threats, tools, and tactics.
For instance, the Certified Information Security Professional certificate must be renewed every three years by obtaining continuing education. The cost of maintaining the certification is only $85 annually. However, this price doesn't reflect the cost of training for recertification or the approximately 120 hours each professional spends on updated training each year.
5. Compliance
Large firms report the average cost to maintain compliance can total up to $10,000 per employee. While compliance regulations safeguard against risks, they create a significant burden for IT and security professionals tasked with maintaining them. Federal, state, and local regulations vary by industry and other factors about your business operations. Gartner estimates that by 2023, 65% of the world's population will have its personal data covered under modern privacy regulations. Some of the most common regulations businesses must follow include:
- HIPAA
- GDPR
- PCI DSS
- CMMC
- FERPA
- COPPA
- GLBA
To maintain compliance with these regulations, companies must follow specific business operations and record-keeping requirements. As a result, the cost of meeting and maintaining compliance comes from many different sources, including:
- Soft costs of preparing for an audit: These costs depend on your current cybersecurity posture and may include preparations necessary to meet requirements, costs of hiring a third-party provider for a gap assessment, costs of devising a security plan, and other costs associated with bringing your organization's security practices up to date.
- Hard costs for tools and services: Depending on the size of your company and your current cybersecurity posture, these costs may include tools that provide multi-factor authentication, log monitoring, data backup, etc. Other hard costs when preparing for an audit might include a professional gap assessment or services from cybersecurity professionals to help your organization create new security processes.
- Hard costs of a third-party audit: A third-party audit is a professional comparison of your business's security processes to the policies outlined in a specific set of regulations. The cost of such an audit will likely depend on the size of your company, market rates, and the specific regulations involved.
The Cost of Non-Compliance
Like most things in cybersecurity, the cost of failure when it comes to compliance can be much higher than the cost of prevention. On average, an organization stands to lose over $235,000 if they face a GDPR non-compliance issue. The maximum civil penalty for violating COPPA is $40,000 for a single individual. While that might seem minuscule if your organization is facing a cost of over $50,000 to achieve compliance, it's important to remember that the fine will be multiplied for every individual involved.
HIPAA violations fall into 4 tiers. Maximum fines per violation in tiers 1-3 are $50,000. For tier 4 violations, $50,000 is the minimum fine per violation. GLBA penalties can result in fines of $100,000 for each violation. Federal non-compliance fines are not the only costs for companies that fail to meet required standards. For instance, violations of CalOPPA (California state privacy laws) can result in a penalty of $2,500 per violation.
The costs of non-compliance do not begin and end with fines. Other lesser known costs of noncompliance include:
- Prison time
- Lawsuits and other legal fees
- Downtime and loss of productivity
- Difficulty in securing capital or financing
- Damage to company reputation
- Lost business partnerships
6. Remote Work Implementation Costs
Pandemic restrictions brought about remote work across practically all industries. Even as restrictions were lifted, successful remote work operations paved the way for a new normal of hybrid workforces for many organizations. 91% of workers in the US working at least some of their hours remotely are hoping their ability to work at home becomes permanent. While 54% are hoping for a hybrid work schedule, 37% would like to work from home exclusively.
Although employees are comfortable working from home, these extended networks present more cybersecurity vulnerabilities. To provide security against long-term risks, organizations will have to deploy new security controls for remote devices. For companies depending on internal resources alone, expanding efficient security practices to remote workers may require increased headcount within your cybersecurity team and additional tools and software applications to protect remote devices. The cost of cybersecurity for remote and hybrid workforces will depend heavily on the size of your company, the sensitive data that requires protection, and your industry regulations.
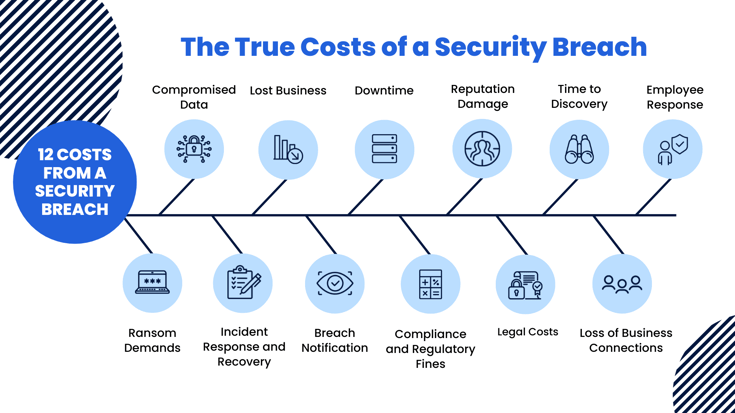
7. The Cost of a Breach or Attack
No matter the cost of your cybersecurity investments, one thing is certain. The cost of a breach or other successful cyberattack will be significantly more expensive. The average cost of a data breach in 2021 was 4.24 million, a 10% increase from 2020. Yet, data breaches in the US average around $9.05 million. The average ransom demand is around $220,298. However, requests for outlandishly high payments have more than doubled, with 11% of companies paying $1 million or more. Unfortunately, these startling figures fail to tell the whole story when uncovering the ongoing costs of a cybersecurity attack. Some costs are much more difficult to estimate. Costs of an attack likely to affect any business include:
- Ransom Demands
- Compromised Data
- Incident Response and Recovery
- Lost Business
- Breach Notification
- Downtime
- Compliance and Regulatory Fines
- Reputation Damage
- Legal Costs
- Time to Discovery
- Loss of Business Connections
- Employee Turnover
8. The Cost of Burnout
It's no surprise that cybersecurity is a high-stress profession. Security professionals face hundreds of alerts daily, many of them false. With enormous task loads, the job becomes a high-stakes game of risk prioritization where a single mistake can lead to a successful attack. In recent years, increased remote work, the use of IoT devices, and cloud adoption have increased workloads for all levels of cybersecurity professionals. In the meantime, a talent shortage combined with burnout means internal cybersecurity teams are shrinking.
Burnout in cybersecurity is becoming increasingly common. There are currently about 435,000 cybersecurity job openings in the US. The unemployment rate in the industry is 0%. Among professionals currently working in the industry, 51% experienced extreme stress or burnout in 2021, and 65% considered leaving their job because of job stress. Only 33% would recommend such a career to others and the same number would also likely discourage people from entering the industry.
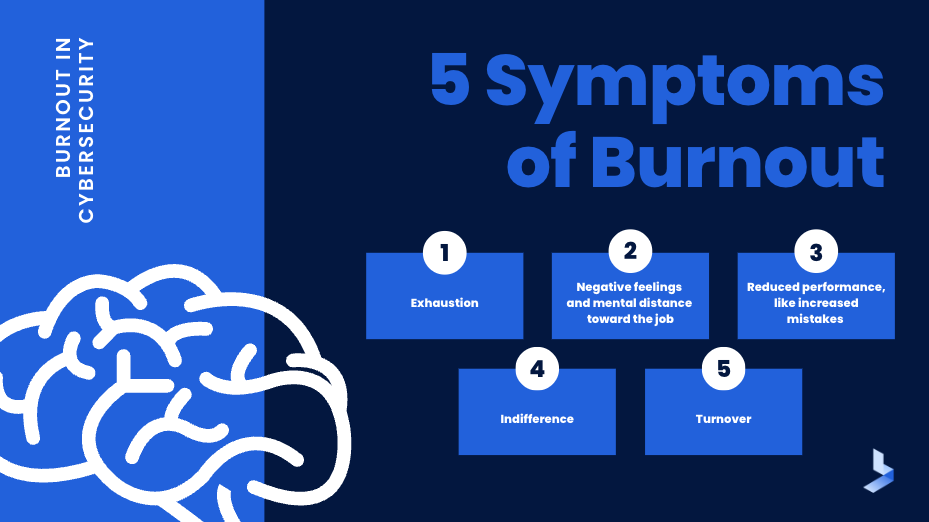
 The cost of burnout for businesses depending solely on internal security teams can quickly add up. Cybersecurity burnout leads to:
The cost of burnout for businesses depending solely on internal security teams can quickly add up. Cybersecurity burnout leads to:
- Poor work performance
- Absences due to stress-related health issues
- Increased salaries to match longer hours
- Recruitment, onboarding, and training costs due to turnover
- The cost of a successful cyberattack due to poor work performance and security gaps left by understaffed teams
9. The Cost of Dwell Time
Modern sophisticated cyberattacks rarely use brute force tactics used to breach your organization's external perimeter. Instead, attackers use discrete methods to quietly infiltrate your network and spend time mining data or reaching an objective that will result in bigger financial gains. These slow and low attacks depend entirely on the amount of time an attacker can spend lurking in your network without being noticed. Referred to as dwell time, the time an attacker spends in your network can lead to larger data leaks or credential theft that can increase a hacker's level of authority.
The average time taken for organizations to contain data breaches in 2021 was 287 days. Breaches with a lifecycle of over 200 days had an average cost of $4.87 million compared to $3.61 million for breaches with a lifecycle of fewer than 200 days. Short-staffed security teams or those depending on multiple tools with minimal integration technologies are less likely to have the resources to recognize suspicious behavior within the network, resulting in longer dwell time and the increased likelihood of an attack.
10. Maintaining 24/7 Monitoring and Response
Cybercriminals don't work office hours. In fact, some of the most successful attacks occur when businesses are closed for the night, weekend, or holidays. As a result, many organizations are beginning to recognize the need for 24/7 cybersecurity monitoring and response. If you're running a fully-staffed SOC, you're probably confident that your business has adequate protection during business hours. Yet, unless your team works 24 hours a day, your organization is unprotected more than half the time.
So, how can businesses close this enormous security gap? If an organization depends on internal resources alone, achieving 24/7 monitoring and response would require an additional security team to work off-hours. Even if both teams worked a maximum of overtime, the business would need to double the budget typically required for an on-prem staff salary. Furthermore, the talent shortage in the industry will likely require high-level salaries and increased benefits for the successful recruitment and retainment of qualified professionals. As a result, your organization would need to increase the budget for recruitment as well.
How MDR Security Eliminates Many of the Cybersecurity Expenses Affecting Your Organization
Managed detection and response is an outsourced cybersecurity option that provides your organization with a security solution customized to the needs of your organization. A collection of services and tools, MDR is a turnkey solution designed to tackle the modern cybersecurity threat landscape and the issues affecting internal IT and security teams of all sizes. MDR is a group of services that offers organizations the protection of an off-site SOC combined with a comprehensive security stack that allows organizations to rapidly detect, analyze, investigate, and actively respond to cybersecurity threats. It also offers many companies a solution that will considerably decrease the upfront and ongoing costs of cybersecurity.
The benefits of MDR security for effective cybersecurity are clear. Let's investigate the ways it reduces the top 10 cybersecurity costs.
- A fully staffed remote SOC is included in the monthly cost of maintaining MDR. Instead of dealing with the increasing recruitment challenges and rising salaries in the industry, you can depend on trained and experienced professionals provided as part of the service.
- MDR is a turnkey solution that includes a preconfigured cybersecurity stack with modern tools and services.
- As a turnkey solution that provides both tools and assistance from cybersecurity professionals, MDR includes the optimization of tools and software included with the service. Organizations can recognize time-to-value in a fraction of the time.
- The remote SOC included with MDR security offers your organization the opportunity to supplement your existing team with experienced professionals that act as an extension of your team. As a result, internal security professionals can gain greater knowledge from working with experienced professionals in your MDR vendor's remote SOC.
- MDR services are tailored to meet the individual security requirements and goals of each organization. While compliance might not be the overarching goal of the service, improved cybersecurity compliance as it relates to your industry can cut some of the major costs associated with cybersecurity compliance maintenance.
- MDR is cloud-based and scalable to meet the needs of any growing business. This growth can include company growth or the protection required to include the addition of devices, infrastructure, and software required for remote work.
- MDR is a fully effective end-to-end solution designed to tackle the complexities of the modern cybersecurity landscape. Utilizing it for your organization means you'll be less likely to become the victim of a successful attack.
- MDR is customizable to provide a complete cybersecurity solution or act as an extension of your existing efforts. By automating specific services and adding the increased cybersecurity headcount offered by an off-site SOC, you can eliminate many of the causes of burnout in cybersecurity.
- Highly effective monitoring and response actions supplied by modern cybersecurity tools and trained experts mean that attackers will have little chance of dwelling in your network for long periods of time without detection.
- MDR works 24/7/365 so your internal team has time to eat, sleep, and go on vacation.
MDR security has the capability to improve your cybersecurity efforts while actually saving your business money. Ready to take the next step with managed detection and response? Download our MDR Buyer's Guide to learn get everything you need to make an informed investment.
